About power transformers
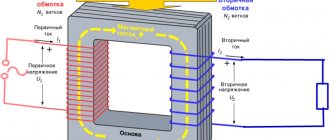
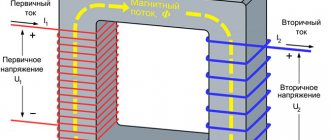
Power transformers are one of the main elements of electrical power supply networks. They perform the task of converting the mains voltage from higher values to lower values (lowering) or from a lower value to a larger value (increasing).
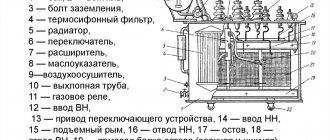
A successful example of a power transformer, familiar to many, is the step-down three-phase oil transformer TMG of sealed design. For example, TMG-25 /15/0.4. This transformer nomenclature means a 25 kVA power transformer, with a high voltage (HV) step down of 15 kV, to a low voltage (LV) voltage of 400 V (0.4 kV).
Brands of power transformers
Let's remember the main brands of power transformers with a capacity of 25-2500 kVA (read the markings in capital letters):
- Three-phase Oil (TM);
- Oil-Sealed (TMG);
- Three-phase Oil Sealed Flange (TMHF);
- TME - three-phase oil for electrical equipment on a mobile base;
- Oil Flange (TMF);
- TMZ - Oil with nitrogen cushion protection;
- OC - Single-phase with oil circulation cooling;
- Etc. and so on.
Work during major repairs of power transformers
- During a major overhaul, all routine repair operations are performed, as well as the following work:
- For explosion-proof transformers and transformer substations, the following work is additionally performed:
- checking the status of locks;
- checking explosion protection elements, shells;
- coating of explosion-proof surfaces with a thin layer of grease CIATIM-202, CIATIM-203.
Repair instructions are given for power transformers for general industrial use with voltages up to 35 kV and power up to 16,000 kVA, transformers for powering converters and electric furnaces, dry transformers; autotransformers with a power of up to 250 kVA, voltage stabilizers for 220–380 V with a power of up to 100 kVA; complete transformer substations with voltage up to 10 kV and power up to 1000 kVA.
Operation and repair of the listed equipment must meet the requirements of PTE and PPB.
To ensure the safety of work during maintenance and repair of power transformers, the personnel involved for these purposes must have a qualification group in accordance with the PTE and PPB.
Source
Maintenance of power transformers
Maintenance of power transformers is carried out as necessary, but at least once every 6 months. Along with the maintenance of the transformer, maintenance of the substation (TS or RP) is carried out.
Regulatory documents provide for three types of maintenance of transformers:
- Control. Carried out for the purpose of preventive identification of possible malfunctions;
- Inspection. Visual inspection of the technical condition of the transformer.
- Unscheduled repairs.
All types of maintenance are carried out by employees who have access to this type of work with strict adherence to safety precautions.
Work during routine repairs of power transformers
- During current repairs, maintenance operations are performed in full, as well as the following work:
Simultaneously with the current repair of transformers, current repairs of bushings are carried out.
Safety precautions when carrying out maintenance of transformers
- Before starting work, the specialist prepares the necessary tools and makes sure that they are in good working order;
- The work is carried out in special clothing with the obligatory use of means of protection against electric shock;
- To ensure safe work, the power supply to the camera being inspected is turned off. The camera switch is turned to the “off” position, a safety sign is hung on the switch that is turned off, warning people about the work;
- Next, the worker discharges the capacitors;
- Having opened the transformer chamber, the worker makes sure that there is no voltage at the LV output of the transformer.
Related articles: Concreting power transmission line supports
Transformer Maintenance Composition
Maintenance of power transformers includes:
- visual inspection;
- checking all important characteristics;
- remote control of temperature conditions;
- carrying out measurements of electrical parameters;
- analysis of materials, including transformer oil;
- checking the condition of welded and bolted connections, ceramic insulators, ground loop of the transformer substation and ground electrodes;
- insulation resistance measurements;
- control of circuit breakers;
- measurements of the phase-zero loop and short-circuit current;
- testing;
- monitoring the operation of automatic backup power input devices;
- inspection of personal protective equipment, relay protection and automation devices, and construction parts of transformer substations.
Technical inspection
During the inspection the following are checked:
- The noise of the transformer. The characteristic hum should not have unnecessary noise in the form of clicks, rattles, or crackles. They indicate the presence of poorly secured parts;
- The oil level glass is inspected. It must be whole;
- Check the oil level and color. The oil should not be dark;
- The entire transformer is inspected for oil leaks. If leaks are detected, the transformer is repaired using a standard repair kit;
- The air drying filter is inspected. The filter indicator (silica gel) in a dry normal state should be blue, not pink;
- Porcelain insulators are visually inspected. They must be intact, without cracks or chips;
- The contact connections of the transformer are inspected. In normal condition, the hardware clamp on the TM transformer and other contacts should not have colored patterns, burns or charring. Their presence indicates poor tightening of the high-voltage and low-voltage pins.
hardware clamp for transformer TM
The presence of traces of charring, melting, carbon deposits, and decomposition of gaskets on the transformer and its parts indicates serious malfunctions of the transformer requiring immediate repair.
The results of the technical inspection are recorded in a journal.
Inspection procedure
The inspection procedure must be followed. The point is not even that the instructions help to strictly follow the plan and not forget about anything, but about convenience and reducing the time required for the procedure.
Load
The transformer load is checked using ammeters. They connect to devices and measure all types of loads that exist. The data will be checked against the tables.
The degree of equipment overheating depending on the load size is understandable. To ensure that there is no increase in temperature, which could lead to breakdown of the unit, systematic monitoring is regularly carried out using ammeter readings. They are supplied to devices with a power of 1000 kVA or more.
Monitoring oil and ambient temperatures
This is the second stage that people pay attention to when it comes to testing production transformers. If work is carried out with indicators higher than permissible (but not higher than the final standard), then the service life of the windings is significantly reduced. Insulating oil becomes unusable when exposed to high temperatures.
To constantly measure the temperature on most vehicles there is a special mercury thermometer. More modern models are equipped with thermal alarms.
According to the standards adopted in Russia, the minimum temperature of operating oil in a power type transformer at an ambient temperature of no higher than 35 degrees should not exceed 95 degrees.
IMPORTANT! In this case, the maximum permissible difference between the temperature of the environment and the oil is 60 degrees.
Oil level and color
The oil level is checked using a special cutoff, which is located on each transformer. There are modern options that automatically read volume information. But if the level can be changed by simply adding oil, then the situation is different if it has lost its color.
The optimal color is from light yellow to golden yellow. This means that there are no contaminants, impurities or other components that change the efficiency of operation. If the oil darkens, a brown or brown tint appears, then it must be replaced. Working with a component of poor quality threatens the failure of structural components.
External condition of insulators
The external condition of insulating materials must be checked. If defects occur, this may affect the safe use of the transformer. The insulator is examined to see if there is:
- cracks;
- traces of ceilings;
- places where mastic leaks; strong creases;
- pollution.
All insulators are checked carefully. When contamination is detected, the nature of its occurrence is calculated.
Checking the grounding condition
The quality of grounding affects the safety of operating personnel. It is checked experimentally, after which they additionally look to see if oil is leaking from the device casing.
Listening to Noise
There will certainly be noise when the transformer is operating. But its characteristics say a lot about the operation of the mechanism. Normally functioning equipment has uniform noise levels, without measuring tone or volume level. The person conducting the inspection must turn off the fans to listen to the noise. If clicks and crackling are heard, a change in tones or an increase in tone is observed, or a decrease in the frequency of volume, then a thorough check is carried out.
Primary voltage control
This indicator is also important for testing, as it determines the efficiency of the mechanism. The permissible maximum excess of the primary voltage indicator is five percent of the norm, which is indicated in the operation sheet. Pay attention to the branch number.
Assessment of the condition of the premises, the degree of compliance with safety regulations
The quality and safety of the transformer’s operation is directly affected by the installed devices and the room itself. Additionally checked:
- whether there are fire extinguishing agents and what quality they are;
- Is the ventilation system working?
- what temperatures are maintained;
- Is the room itself in good condition, are there any drafts, etc.
Typically, this characteristic is practically skipped during a routine inspection, leaving only a check of the date of fire extinguishing agents.
No oil leakage
During an external inspection, they check not only the condition of the oil (its level and color), but also the absence of leaks. Even minimal release of the composition leads to a decrease in the productivity of the device. In addition, the risk of getting injured at work increases.
State of silica gel
Leakage or changes in the composition of silica gel occur quite rarely, but still this characteristic is taken into account during a routine inspection. Defects can lead to contamination and failure of structural components. Therefore, silica gel is replaced.
Integrity of oil glass
The oil gauge glass allows you to determine the oil level, which affects the efficiency of the functionality. The integrity of the glass is important for correct operation and convenient display of information.
Professional assistance for transformer maintenance
Only specially trained high-profile electrical technicians who have permission to perform such work and are in good health at the time of maintenance are entitled to carry out maintenance of transformers. When carrying out such work, protective clothing and a set of special tools are used.
The engineer has a license to carry out maintenance of transformers, carry out inspection and repair work. We have a staff of highly qualified specialists and all the necessary tools to identify and promptly resolve problems. We will be happy to help you!
The functional purpose of power transformers is to convert the network voltage to the required value - up or down. This is the basic part of any electrical network. Regular maintenance of current transformers will help maintain their performance.
Safety regulations
Servicing instrument transformers without observing safety regulations is a big risk. Neglect of safety precautions on the part of the employer can endanger the health and life of service personnel. Power transformers require high professionalism when working with them. Employees involved in this area of work must have access to electrical operations. According to the rules, maintenance of instrument transformers can only be carried out in special clothing and with PPE.
In addition, illiterate adjustment of parameters is fraught with the occurrence of an emergency situation. Transformer failure can lead to downtime and, accordingly, large losses for the enterprise.
Maintenance work on oil and dry transformers
Maintenance and repair of transformers is carried out in accordance with the standards of current documents - GOST, PTE, TU, technological instructions, technical guidelines, operating and repair instructions. Approximate maintenance work for transformers depending on their type is given in the table.
Type of transformers serviced
Maintenance work
Oily
Analysis of transformer oil, topping it up or replacing it;
broaching bolted connections;
high-voltage tests of windings;
measurement of winding resistance and transformation ratio;
preparation of a report on the results of measurements.
Dry
Visual inspection of end adapters, winding insulation, leads;
checking bolts, high-voltage cells, noise levels;
checking voltage and currents at the input and output of windings;
control of compliance of operating currents and voltage with standard indicators;
determination of transformation ratio and insulation resistance of windings.