Design of a standard circuit breaker
For example, we will use the BA47-29 series switch as the most popular switching device with an affordable pricing policy. Before you learn how to properly connect a circuit breaker to a single-phase network, you need to consider its design.
The BA47-29 series circuit breaker consists of the following elements:
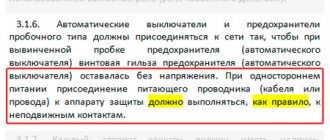
- A copper terminal connected to a fixed power contact. Most often, the supply wire is installed exactly in this place.
- The movable contact, which makes the switching, and the copper stranded conductor, has a sufficiently large cross-section.
- Arc chamber.
- A special thin plate with a hole through which gases formed after the arc escape.
- An electromagnetic release, presented in the form of a simple coil. The stranded conductor from the moving contact is soldered to the coil.
- Plastic, fully dielectric handle.
- A bimetallic plate that acts as a thermal release. The plate is located immediately behind the reel.
- A special screw for adjusting the bimetallic plate. The screw is not installed on all models, and adjustment is made at the manufacturer.
- The lower copper terminal, from which the conductor goes directly to the consumer.
A three-phase machine has a similar design, but instead of one terminal, it uses three, isolated from each other.
What are circuit breakers
These are specially designed devices whose main task is to protect wiring from melting. In general, automatic machines will not save you from electric shock and will not protect your equipment. They are designed to prevent overheating.
- The method of their operation is based on opening the electrical circuit in several cases:
- short circuit;
- exceeding the current flowing through a conductor not intended for this purpose.
As a rule, the machine is installed at the input, that is, it protects the section of the circuit that follows it. Since different wiring is used for wiring different types of devices, this means that protection devices must be able to operate at different currents.
At first glance, it may seem that it is enough to simply install the most powerful machine and there will be no problems. However, it is not. A high current, for which the protection device does not respond, can overheat the wiring and, as a result, cause a fire.
What does the machine consist of?
- A typical machine consists of the following elements:
- Cocking handle. Using it, you can turn on the machine after it has been triggered or turn it off to de-energize the circuit.
- Switching mechanism.
- Contacts. Provide connection and breaking of the circuit.
- Terminals. Connect to a protected network.
- A condition-triggered mechanism. For example, a bimetallic thermal plate. Many models may have an adjusting screw to adjust the nominal current value.
- Arc extinguishing mechanism. Present at each pole of the device. It is a small chamber in which copper-plated plates are placed. On them the arc is extinguished and comes to naught.
Depending on the manufacturer, model and purpose, machines can be equipped with additional mechanisms and devices.
Trip mechanism design
The machines have an element that breaks the electrical circuit at critical current values.
- Their operating principle can be based on different technologies:
- Electromagnetic devices. They are characterized by a high speed of response to a short circuit. When currents of unacceptable magnitude are applied, the coil with the core is activated, which, in turn, turns off the circuit.
- Thermal. The main element of such a mechanism is a bimetallic plate, which begins to deform under the load of high currents. By bending, it has a physical effect on the element that breaks the chain.
An electric kettle works in approximately the same way, which can turn itself off when the water in it boils. There are also semiconductor circuit breaking systems. But they are used extremely rarely in household networks.
Time-current characteristics of circuit breakers
The devices differ in the nature of their response to an excessively high current value. There are 3 most popular types of slot machines - B, C, D.
- Each letter means the sensitivity coefficient of the device:
- B (from 3 to 5 xln);
- C (from 5 to 10 xln);
- D (from 10 to 20 xln).
What does it mean? It’s very simple - to understand the range at which the machine is capable of operating, you need to multiply the number next to the letter by the xln value.
- So for the B16 machine gun:
- 16*3=48A;
- 16*5=80A.
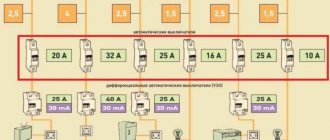
- Let’s take, for example, three machines with the same rated current of 16A, but different time-current characteristics:
- the machine marked B16 will turn off in the range 48...80A;
- marked C16 will turn off in the range 80...160A;
- and marked D16 will turn off in the range 160...320A.
The most common type of machine is C, it is used in almost every home. Machines marked D are used mainly in places with consumers that have large starting currents, for example, electric motors. Type B is the most sensitive and is rarely used, mainly to protect electronic equipment. And it costs correspondingly more.
At a current of 100 A, the B16 circuit breaker will turn off almost instantly, while the C16 will not turn off immediately, but after a few seconds from thermal protection (after its bimetallic plate heats up).
Legend
Different types of machines are marked in their own way for quick identification and selection of the one needed for a specific circuit or its section. As a rule, all manufacturers adhere to one mechanism, which allows them to unify products for many industries and regions.
- Let’s take a closer look at the signs and numbers printed on the machine:
- Brand. Usually the manufacturer's logo is placed at the top of the machine. Almost all of them are stylized in a certain way and have their own corporate color, so choosing a product from your favorite company will not be difficult.
- Indicator window. Shows the current status of contacts. If a malfunction occurs in the machine, then it can be used to determine whether there is voltage in the network.
- Machine type. As already described above, it means a shutdown characteristic at currents significantly exceeding the rated current. C is used more often in everyday life and B is used a little less frequently. The differences between the types of electric machines B and C are not so significant;
- Rated current. Shows the current value that can withstand a long-term load. Rated voltage. Very often this indicator has two meanings, written separated by a slash. The first is for a single-phase network, the second is for a three-phase network. As a rule, in Russia a voltage of 220 V is used.
- Switch-off current limit. It means the maximum permissible short circuit current at which the machine will turn off without failure. Current limiting class. Expressed in one digit or absent altogether
- Scheme. On the machine you can even find a diagram for connecting contacts with their designations. It is almost always located in the upper right part. Thus, by looking at the front of the machine, you can immediately determine what type of current it is intended for and what it is capable of.
Which type of machine to choose
When choosing a protective device, one of the main characteristics is the rated current. To do this, you need to determine what current strength is required by the totality of all consumer devices in the house.
And since electricity flows through wires, the current required for heating depends on its cross-section. The presence of poles also plays an important role.
- The most commonly used practice is:
- One pole. Circuits with lighting devices and sockets to which simple devices will be connected.
- Two poles. It is used to protect wiring connected to electric stoves, washing machines, heating appliances, and water heaters. It can also be installed as protection between the shield and the room.
- Three poles. Used primarily in three-phase circuits. This is relevant for industrial or near-industrial premises. Small workshops, production and the like.
The tactics for installing machine guns proceed from larger to smaller. That is, first it is mounted, for example, double-pole, then single-pole. Next come devices with power that decreases at each step.
Wiring
Ideally, if the machines are located next to each other on a DIN rail, then these distances can be measured simply by attaching a conductor so that the transition part from one machine to another forms a loop. This will allow the wire to exit the housing vertically.
The stripped area should be twice as long as the end of the wire, because we will have to make a small loop out of it, which will be used to connect the machine. You will need to put heat-shrink tubing on this loop or tightly wrap it with electrical tape at the place where the insulation ends. This will give our wire rigidity.
Then the loop must be inserted into the contact hole of the machine and tightened tightly. The cleaned areas should correspond to the number of circuit breakers. But we will be sure that the phase is separated correctly - the same for the apartment.
Circuit breakers: design and principle of operation
Before we consider the procedure for connecting circuit breakers in an electrical panel, let’s figure out how they are designed and on what principle they are triggered.
The product includes the following elements:
- Frame.
- Control system.
- Top and bottom terminals.
- Switching device.
- Arcing chamber.
Fire-resistant plastic is used as material for the manufacture of the housing and control system. The switching device contains moving contacts as well as fixed contacts.
An arc-extinguishing chamber is installed on a pair of contacts, which are the pole of the packetizer. When the contacts break under load, an electric arc occurs, which is extinguished by the camera. The latter consists of steel plates, insulated from each other and located at the same distance. The chamber plates help cool and extinguish the electric arc that appears during malfunctions. Machines can have one, two or four pairs of contacts.
Two-pole circuit breakers have two pairs of contacts: one is movable, the other is fixed.
Such a switch is equipped with a position indicator, which makes it easy to find out whether the machine is on (red light) or off (green).
The operating principle of circuit breakers is clearly shown in the video:
Main types of circuit breakers
Place the RCD connection diagram on its body. Such a danger in the form of poor contact carries the threat of melting of the insulation, not only of the wire, but also of the machine itself, which can lead to a fire. Using the example of AB series BA, manufactured by Iek, you can make sure that the upper contact is fixed, respectively, the lower one will be movable. So, we’ve sorted out the installation of the box itself, now let’s figure out how the electrical panel circuit is arranged.
The differences between types of electric machines B and C are not so significant; Rated current. Let's take a closer look at the signs and numbers printed on the machine: Brand.
The voltage from the second input circuit breaker is supplied to a three-phase RCD, the lower terminals of which are connected to a three-phase load.
The main working part is a bimetallic plate.
If you don’t figure it out, write me and I’ll give you a hint.
A wire designed for the household appliance used must have a cross-section that is twice the load.
Shows the current status of contacts. Electrical diagram for connecting circuit breakers.
See also: How to use the device
How does an RCD work?
To better understand how an RCD works, first of all, you should familiarize yourself with its circuit design and internal structure. Regardless of the connection method ( RCD without grounding or with one), the operation of this device is based on the principle of comparing incoming and outgoing currents. For this purpose, it contains a differential unit through which currents I1 and I2 flow in different directions.
Operating principle of RCD
They create identical magnetic fluxes in the ferrite core coils, compensating each other. As a result, the differential signal does not affect the actuator, and the RCD remains in the on (closed) state.
In case of accidental contact with a bare wire, a leakage current Iу begins to flow through the body of a person or animal. As a result of this, the reverse component I2 flowing through the comparison organ decreases by this amount.
The balance of forward and reverse flows in coils F1 and F2 is disrupted, and a difference signal is sent to the actuator unit. After this, the RCD in the two-wire network disconnects the load from the supply line (the dangerous voltage disappears).
Connecting a residual current device to a two-phase network
The case is exotic. Two-phase power supply networks were abandoned at the beginning of the twentieth century. The chance of a modern electrician encountering them is close to zero. It is worth thinking about connecting an RCD to a two-phase network as an elective.
Each pole of the socket is phase. It has a potential to ground of approximately 127 volts. The connection diagrams for residual current devices are similar to single-phase ones. But the circuit breaker must be mounted on each of the two incoming phases. Of course, it is impossible to connect one of the supply wires to grounding or the electrical panel housing.
Additional Information. Two-phase power supply to residential buildings is a thing of the past. However, many modern low-power transformers have windings designed from 380 V. It operates from 2 phases. Typically these are transformers for auxiliary needs in industrial equipment. It is not practical to install a separate RCD for them.
Connection diagrams
So, the operating principle of the circuit breaker is now clear, you can proceed directly to its connection diagrams. Let's start with the fact that machines can be connected to single-phase and three-phase networks. What machines are needed for this? If the conversation is carried out from single-phase networks with a voltage of 220 volts, then either a single-pole device or a two-pole device is usually installed in them. The circuit itself will depend on whether it uses a ground loop or not.
If two wires enter the house (zero and phase), then a single-pole version can be installed in the distribution cabinet. In this case, the phase circuit will pass through the machine itself. If three wires enter the house (phase, neutral and ground), then the common circuit breaker must be two-pole. That is, a phase is connected to the first terminal of the device, and zero to the second. Grounding is routed to consumers (lights and sockets) through a separate terminal box. Next, the wires from the circuit breaker are routed to the meter, then to single-pole circuit breakers installed in groups, but as described in the first case. By the way, below is the system for connecting the machine.
As for the three-phase network, in this case it is best to install three-pole or four-pole structures. Everything here is exactly the same as in the case of a single-phase connection. That is, if the house uses wiring without grounding, then three phases of the power supply are connected to the fixed contacts. The neutral wire is routed as a separate circuit to consumers (sockets and lamps). If the house has a grounding system, then a four-pole model is installed, that is, three phases and zero will be connected to the device, and the grounding loop will go as a separate line to consumers.
Basic mistakes when connecting machines
- Let's look at the most common errors:
- connecting the ends of the cores of a flexible stranded wire without termination;
- insulation coming into contact;
- connecting wires of different sections to one terminal;
- soldering the ends of the cores.
Connecting the ends of the cores without terminating
The main mistake when connecting machines is the use of a flexible stranded wire without termination. It's easier and faster, but not correct. It is impossible to clamp such a wire reliably; over time, the contact weakens (“flows”), the resistance increases, and the junction heats up.
It is necessary to use lugs on a flexible wire or use a rigid single-core wire for installation.
Contact with insulation
Everyone knows that before connecting the machine in the panel, you need to remove the insulation from the connected wires. It would seem that there is nothing complicated here, I stripped the core to the required length, then we insert it into the clamping terminal of the machine and tighten it with a screw, thereby ensuring reliable contact.
But there are cases when people are perplexed why the machine burns out when everything is connected correctly. Or why the power in the apartment periodically disappears when the wiring and filling in the panel are completely new.
One of the reasons for the above is that the wire insulation gets under the contact clamp of the circuit breaker. Such a danger in the form of poor contact carries the threat of melting of the insulation, not only of the wire, but also of the machine itself, which can lead to a fire.
To eliminate this, you need to monitor and check how the wire is tightened in the socket. Correct connection of circuit breakers in the distribution board should eliminate such errors.
Cores of different sections per terminal
Never connect machines with jumpers and cables of different sections. When tightening the contact, the core with a large cross-section will clamp well, and the core with a smaller cross-section will have poor contact. As a result, the insulation melts not only on the wire, but also on the machine itself, which will undoubtedly lead to a fire.
- An example of connecting circuit breakers with jumpers from different cable sections:
- The first machine receives a “phase” with a 4 mm2 wire,
- and other machines already have jumpers with 2.5 mm2 wire.
As a result, poor contact, increased temperature, melting of insulation not only on the wires, but also on the machine itself.
For example, let's try to tighten two wires with a cross section of 2.5 mm2 and 1.5 mm2 into the terminal of the circuit breaker. No matter how hard I tried to ensure reliable contact in this case, nothing worked. A wire with a cross-section of 1.5 mm2 dangled freely and sparked.
Soldering the ends of the cores
Separately, I would like to dwell on this method of terminating wires in a shield, such as soldering. Human nature is such that people try to save money on everything and do not always want to spend money on all kinds of tips, tools and all sorts of modern small things for installation.
For example, consider the case when an electrician from the housing office, Uncle Petya, wires the electrical panel with a multi-core wire (or connects outgoing lines to the apartment). He does not have NShVI tips. But you always have a good old soldering iron at hand.
And the electrician, Uncle Petya, finds no other way out than to tin the multi-wire core, pushes the whole thing into the contact clamp of the machine and tightens it with a screw. Why is it dangerous to connect circuit breakers in a distribution board?
When assembling distribution boards, DO NOT solder or service the stranded core. The fact is that a tinned connection begins to “float” over time. And for such contact to be reliable, it must be constantly checked and tightened. But as practice shows, this is always forgotten.
The soldering begins to overheat, the solder melts, the joint weakens even more and the contact begins to “burn out.” In general, such a connection can lead to a FIRE.
How to choose a machine?
Before you begin installing protective circuit breakers, you need to select them and also understand the intricacies of connection. People who want to know how to wire a circuit breaker ask various questions. For example, are the circuit breakers in the distribution board connected before or after the meter? Should an automatic input be installed? These and other connection nuances are of interest to users.
Basic parameters of circuit breakers
The characteristics of circuit breakers include:
- Rated current value (in Amperes).
- Operating voltage of the electrical network (in Volts).
- Maximum short circuit current.
- Ultimate switching capacity.
- Number of poles.
The maximum switching capacity is characterized by the maximum permissible value at which the switch is capable of operating. The PKS of household devices can be 4.5, 6 or 10 kA.
When choosing, they are most often guided by such basic indicators as short-circuit shutdown current, as well as overload current.
The cause of overload is the connection to the electrical network of devices with excessively high total power, which leads to exceeding the permissible temperature of contact connections and cables.
Taking this into account, it is necessary to install a packet in the circuit, the value of the shutdown current of which is not less than the calculated value, and better - if it slightly exceeds it. To determine the calculated current, you need to sum up the power of the devices that are supposed to be connected to the circuit (for each of them this indicator is available in the passport). The resulting number must be divided by 220 (the standard voltage value in a household network). The result obtained will be the value of the overload current. It should also be taken into account that it should not exceed the current rating that the wire can withstand.
The magnitude of the shutdown current during a short circuit is the indicator at which the circuit breaker is switched off. The short-circuit current is calculated when designing the line using formulas and reference tables, as well as using special equipment. Based on the obtained value, the type of protection is determined. At small sites and in household networks, type B or C machines are used.
Advantages and disadvantages
Two-pole circuit breakers provide control of lines with single-phase power supply, as well as protection of equipment operating in three-phase circuits.
The advantages of these devices include:
- reliable protection of homes, offices and industrial premises from network surges;
- the ability to control the power of individual electrical appliances and installations;
- ease of installation and maintenance. Two-pole AVs are ideal for branching and structuring wiring in the electrical supply of premises.
Of course, the main advantage is that a two-pole circuit breaker simultaneously de-energizes two conductors, regardless of which of them the accident occurred. This guarantees a complete absence of voltage in the protective conductors.
Disadvantages include:
- there is a possibility of cable breakdown when two loaded lines are turned on simultaneously;
- in rare cases, if the thermal release fails, an arbitrary power outage is possible even in the rated voltage mode;
- the need to select two-pole circuit breakers in accordance with the design parameters of the network. If the sensitivity of the switch is too high, it will often trip without good reason, and if the speed of reaction to an unusual situation is too low, the machine will not notice the network overload.
Thanks to the unique advantages, the use of two-pole switches is justified even taking into account the existing likelihood of the manifestation of these disadvantages.
Connection rules
To install a residual current device yourself, you must adhere to a number of rules. The most important of them are the following:
- When installing wiring, you must strictly follow the diagram. The wires are connected according to their letter or color marking. Ideally, the installer should have a diagram on hand.
- The residual current device is connected only after the input circuit breaker. Connecting to the network without a machine is unacceptable.
- You should pay attention to the technical characteristics of the connected RCD. If currents of 20-25 A flow in the network, then the protective device is selected for at least 32 A.
- It is prohibited to use heating radiators or water pipes as a grounding conductor. Such a negligent approach can lead to death for one of the neighbors.
- The general rule is that all electrical installation work is carried out with the voltage removed, except in cases in which disconnection is impossible.
Circuit breaker connection diagrams
The classic option is to include automatic modular switches in the network circuit by placing them in a distribution board. Fastening is carried out on a factory din-rail located horizontally inside the shield. Wires leading to the load are inserted into the space between the rail and the rear wall of the cabinet. They are connected to the lower output contacts of the machines, and the wire from the output of the input machine is connected to the input, upper contacts.
DIN rail mounting of circuit breakers is considered the simplest and most effective technology today.
A channel is made on the back wall of the machine for the rail, the upper edge of the case clings to the rail and by pressing on the front plane of the case, a lever with a spring fixes the lower part of the case to the rail. The machine is removed from the rack in the reverse order, the lever is pulled back, the lower part of the body is retracted, lifting it up, thus the entire body is removed from the rack.
Tip No. 1 High-power input circuit breakers that are not equipped with DIN-rail mounting are separately mounted on a metal plate installed in the panel with holes and threads for bolts. Holes in the machine body for fastening to the shield body are provided by the design; metal screws can be used.
Single-pole circuit breakers
Connecting single-pole circuit breakers is considered the simplest; they are connected to socket and lighting groups.
The phase wire, grounding and neutral conductors are connected through the circuit breaker; they pass directly to lighting fixtures and sockets.
Two-pole machines
More powerful devices, such as electric stoves, heating boilers, shower cabins, split systems and others, where it is necessary to ensure a complete circuit break, neutral and phase wires are connected through two-pole devices.
Three-pole circuit breakers are used in three-phase networks using powerful devices with an appropriate 380V power supply. These can be heating elements, electric motors and others. When, when the rated current is exceeded, all three phases are disconnected, thus eliminating phase imbalance in the entire circuit when the current is exceeded in one of the three lines.
The load is connected to the circuit breaker according to a star circuit without a neutral wire; in this case, the circuit breaker is installed individually for a specific type of equipment.
Four-pole circuit breakers are connected to a three-phase network as input circuit breakers, where the phases are used as separate network lines with individual load elements. In this case, it is necessary to try to distribute the magnitude of the load currents evenly among the phases to avoid phase imbalance. To remove excess currents, a neutral wire is used, a circuit with a grounded neutral.
Which is correct: machine before or after the counter
To answer this question, you should also refer to the PUE, namely to paragraph 1.5.36, which states that for the safe installation and replacement of meters in networks up to 380 V, a circuit breaker must be installed in front of them (at a distance of no more than 10 m) . And this same machine in front of the meter acts as a switching device to disconnect the entire apartment or house, and its nominal values must be appropriate.
The number of machines after the meter is determined directly by the owner of the apartment or house, or by the design organization performing the installation of electrical wiring. There are such electrical panels, the number of devices in which reaches 40-50 pieces, and this is without RCDs and differential circuit breakers. When installing an introductory machine before the meter, the same one can be installed after it. This will not affect the operation of the metering device in any way.
Important! Only representatives of energy supervision authorities can connect the electric meter to the network. Therefore, before connecting an apartment, you should find such an organization in your city and formally call a specialist.
We connect the wires to the machine - a cable with a monolithic core
You can combine living quarters under one machine, hang a boiler on another, an air conditioner on a third machine, etc. Methods for checking RCDs Installation of an electrical panel An electrical panel in an apartment, its importance in the power supply system of the house is extremely great.
Rated voltage. Before us is an automatic machine of the BA series from iek.
The phase wire, grounding and neutral conductors are connected through the circuit breaker; they pass directly to lighting fixtures and sockets.
All that remains is to apply voltage, turn on all protective devices and check the voltage at the output and input of the machine using an indicator screwdriver. Connecting machines in the panel, input from above or below Before connecting the machine from above or below, it is recommended to inspect the connecting sockets. Installing an RCD where children are present is extremely useful.
What is important to do And now you have come to perhaps the most crucial moment - filling out the shield. What does the PUE say about this? It can also be installed as protection between the shield and the room.
Operating current indicator. Conclusions and useful video on the topic Nuances of installing all elements on the apartment panel: Details of installation of RCDs: RCDs and automatic devices are technically complex equipment. Moreover, each group needs a machine gun with its own characteristics. For work carried out in the panel, it is worth preparing all jumpers of the required length, as well as the appropriate cross-section.
What does the PUE say about this? These are protective shutdown systems, various relays, circuit breakers and multifunctional machines. Such a danger in the form of poor contact carries the threat of melting of the insulation, not only of the wire, but also of the machine itself, which can lead to a fire.
You need to look at pins 1 and 3, if you look from left to right, the cores of the supply wires are connected there. The conductors are not connected correctly. Connection diagram for DIFAVTOMATO.
Features of connection with and without grounding
Some experts sometimes express the opinion that connecting an RCD without grounding is impossible or that such a circuit will be inoperative.
This is a gross mistake and misconception for the following reasons:
- The operating principle of the residual current device initially refutes this version, since grounding does not play any significant role in it.
- Some people with little experience implement a circuit with grounding in such a way that it does not function, that is, they actually get a connection without grounding, but the RCD continues to fully perform its tasks.
- Leakage to a grounded object is possible in both cases, and this probability does not affect the operation of the emergency system, since the device will de-energize the circuit exactly at the moment when the current reaches the rated value.
Based on this, the following conclusions can be drawn:
- The presence of an RCD increases the level of safety when operating household items without grounding.
- The disconnect device itself will perform its basic functions without grounding.
In any case, the highest degree of safety will be achieved only with a combination of RCD and grounding, but in its absence, the installation of such a device becomes even more important and relevant.
How to check an RCD in 30 seconds
The residual current device is responsible for the health and safety of people, so it should be checked periodically for proper operation. For this purpose, the device has a “test” button. If, when pressed, the RCD knocks out, then it is considered to be in good working order.
Machine with “test” button
There is another more reliable verification method. To do this, you need to connect a resistor between the ground and the phase wire of the socket. The resistor resistance is selected based on Ohm's law and the RCD operating current. The method is extremely dangerous for the tester. It is not recommended for use by people who do not have education or experience as an electrician.
Sequence of operations for connecting a circuit breaker
- The section of the network into which the circuit breaker is connected is de-energized by a switch or an input circuit breaker. The presence of voltage is checked with an indicator screwdriver, a multimeter or other indicator device. After this you can start working;
- The circuit breaker is fixed on a DIN rail located in the distribution board;
- From the ends of the wires connected to the switch terminals, the insulation is removed to a depth of 8 mm to 1 cm.
Tip #2. It is necessary to strip the insulation to the depth of the contact terminal, as far as the end of the wire is immersed there; the exposed wires should not protrude beyond the switch body. Anything less is also not recommended; the clamping screw may rest against the insulating layer and the contact area will not be sufficient to ensure reliable contact. In this case, the connection will heat up and the machine will fail.
- In the two-pole model of the switch, the neutral and phase wires are connected to the terminals of the corresponding designation on the upper contacts;
- The phase and neutral wires going to the load are connected to the lower output terminals;
- The wires in the contact sockets are tightened with bolt clamps;
- After the connection, you can connect the power and check the functionality of the switch.
Machines with a different number of poles are connected in a similar way.
How to install an RCD: before or after the machine
The residual current device is a very useful switching device that requires correct installation, otherwise its operation may be unstable. If the installation is carried out incorrectly, then at the first short circuit in the apartment you will need to replace the RCD, which is an order of magnitude higher in cost than any circuit breaker.
There is no particular difference whether the RCD will be located before or after the machine. But the issue can be considered from a practical perspective. Any residual current device does not have protection against short circuit currents, and if you install it without a circuit breaker, the consequences can be very different, including damage to the device.
Therefore, it is best to install an RCD immediately after the introductory machine, but before the packetizer, the line from which will go directly to the consumer. This will provide reliable protection of the circuit from short circuits, and users from the unwanted action of operating potential when a phase wire gets into contact with the housing of a household appliance.
Connection diagram for machines in the panel
The layout of the panel in the apartment is one of the main points, but before we deal with it, let's see what elements are included in the design. So that you can understand the symbols and composition of the wiring diagram.
- Typically, when installing a shield, use:
- Introductory machine.
It is placed to protect the entire wiring circuit. The cores of the main incoming cable are connected to the terminals of the input circuit breaker. For convenient work with the electrical panel, a switch is often installed in front of the input circuit breaker.
It allows you to de-energize the entire assembly to replace elements, safe preventative maintenance, and completely shuts off the power supply to your apartment or house. In this case, the power cable is connected to the switch.
- Electric meter.
It is installed after the introductory machine and calculates the energy consumption in a house or apartment. Sometimes the meter stands separately, up to the panel, along with a circuit breaker. For example, on the site of an apartment building.
- Residual current device - designed to protect against electric shock and prevent fires.
The RCD in the circuit can be one, installed after the meter, for example, in a one-room apartment with a small load. Or they install several RCDs on separate lines with high consumption (for an electric stove, washing machine, air conditioner).
- Linear machines.
Needed for separate lines for different rooms, household appliances and lighting. They break the circuit if an overcurrent or short circuit is detected, protecting the wiring and connected equipment from damage. Triggering the machine can prevent a fire due to heating and ignition of the wire.
- Diffautomatic protection.
It can be installed instead of a pair of automatic circuit breaker + RCD on separate power lines of electrical appliances.
- DIN rail is a mounting element for installing equipment.
Attached to the rear wall of the electrical panel housing. Depending on the dimensions of the cabinet, the number of DIN rails and the possible number of installed modules may vary. In order not to make a mistake when purchasing a switchboard housing based on the number of modules, you need to draw up a wiring diagram.
- Connecting busbars.
Needed for disconnecting the electrical panel and connecting working zeros and grounding wires. The panel uses both neutral terminal bars and grounding ones.
- Distribution buses.
Installed for a “bundle” of linear machines, RCDs, and automatic circuit breakers. Comb busbars have reliable insulation and allow you to quickly and safely connect a number of machines through the input terminal block. They can be used both for the current conductor and for the working zero.
Methods for installing RCDs
There are two possible ways to install the device. The first option involves installing a common RCD in the electrical wiring diagram, immediately behind the meter and the machine. With one common RCD for an apartment or house, it is very difficult to find the place of current leakage through the insulation of the wires. Such a violation of insulation should be looked for throughout the apartment or cottage.
Variant of electrical wiring diagram with a common RCD and protective grounding in a single-phase network
In this case, the RCD will de-energize the entire apartment. In another option, several RCDs are installed, separately for each direction of electrical wiring, in the living room, kitchen, bedroom and children's room. This circuit of separate electrical wiring for rooms is assembled in the electrical panel in the hallway.
Several RCDs are installed in the same electrical panel. This option is of course expensive, but it has some advantages. Firstly, when the RCD is triggered, the network will be turned off in only one direction, and in the other part of the apartment the network voltage will remain. It will be easier to look for electrical damage in one room.
Electrical wiring diagram option with a separate RCD for sockets and protective grounding in a single-phase network
In a children's room, a separately connected RCD device will protect children from touching a dangerous socket faster than in the version of a common RCD. For the children's room option, an RCD with a shutdown current of less than 10 mA is installed. In the bathroom or kitchen where the washing machine is located, you need to install an RCD with a high response current (300mA - 500mA), because an RCD with a shutdown current of 10 mA will constantly turn off the kitchen.
The RCD is selected according to the optimal current for all loads in amperes. The response time of an RCD - a high-quality device - is up to 0.1 seconds, during which time an electric shock is not felt. The protection device must be checked for functionality by pressing the RCD test button once a month and after each emergency operation.
How to connect a machine in a panel: select and connect the machine correctly, recommendations
If you ask any person inexperienced in electrical engineering what is in an electrical panel, the immediate answer will be - automatic machines. Although, in addition to circuit breakers (this is the correct name for machines), there may be RCDs, differential circuit breakers, load switches, contactors, pulse relays and much more. The purpose of this article is to find out how to select automatic circuit breakers from the whole variety of modular devices, what they are intended for, how to choose them correctly, how to connect the circuit breaker in the panel and what to do when triggered.
How to connect a machine in a panel
Why does the average consumer need knowledge about circuit breakers?
At first glance, it may seem that an ordinary person, completely unfamiliar with engineering in general and electrical engineering in particular, does not need to know anything about circuit breakers, because the wiring in an apartment or house was done by professionals. It is possible that this is so, but what will a person do if the voltage suddenly disappears in the entire apartment or house or in some part of it? Of course, the person will open the panel, look at which machine was “knocked out”, and again move the lever to the “on” position.
It is in this action that the main mistake of “ordinary people” lies, because before turning on a triggered modular device, you need to understand the reason for its operation. Therefore, you should not be surprised when, after turning on again, you immediately or after some time turn off again. Without eliminating the cause, you should never re-enable modular devices, including circuit breakers (hereinafter referred to as circuit breakers). This can lead to dire consequences both for human health and life, and for property.
Something is clearly wrong with the circuit breaker in this apartment.
The fact is that different protection devices are assigned their own functions, therefore the reasons for the operation of automatic circuit breakers and residual current devices (RCDs) are completely different. And in most cases this does not apply to the quality of electrical wiring installation. Of course, an experienced electrician will always find the reason. But if incidents with electricity occur at night or on a weekend, then not every electrician will agree to quickly solve the problem, and if he does, the owners will have to pay well out of their own pockets for the urgency.
As the electricians themselves say, 50% of cases of protection devices tripping are trivial and occur through the fault of the owners themselves, and electrical wiring has nothing to do with it. That is why elementary basic knowledge about protection devices, their purpose and the rules for responding when they are triggered will be very useful. The authors of the article will try to explain everything in an understandable language, without going into the jungle of technical nuances that will be of interest only to specialists, but not to “ordinary people.”
What is a circuit breaker and what is it for?
A circuit breaker (circuit breaker) is a device that is designed to switch (in other words, turn on and off) an electrical circuit. That is, what is meant here is that you can manually turn on and off an electrical circuit using a lever.
Circuit breakers with different numbers of poles
However, the name itself - circuit breaker - indicates that the machine should automatically turn off the load. In what cases does this happen?
- When the circuit protected by the circuit breaker flows a current that exceeds the permissible one. And the greater the current excess, the faster the shutdown occurs.
- When very large currents arise in the protected circuit that are unusual for the load - the so-called short circuit currents. In these cases, the machine reacts very quickly - within a fraction of a second.
Overload can occur when, in one circuit protected by a circuit breaker, one powerful load is turned on at the same time, for which neither the cable nor the circuit breaker is designed, or several powerful loads. For example, in one socket circuit of six sockets, an electric kettle, iron, electric fireplace, microwave oven, steamer and hair dryer are simultaneously turned on. Naturally, with such a load, the current will greatly exceed its rated values, this will cause the wires to heat up greatly, which can lead to melting of the insulation and subsequently to a short circuit. The machine should not allow this to happen and should turn off the circuit before the wires get too hot.
A short circuit can occur in both the socket and the light bulb socket.
Short circuit currents can occur when in any device there is a breakdown of the insulation on the housing or the phase and neutral conductors are short-circuited. According to Ohm's law, the lower the resistance, the greater the current. The higher the current, the more heat is generated, which leads to melting and burning of the insulation. A short circuit is the most common cause of fires in electrical wiring. That is why the machine is entrusted with a very important function - to instantly respond to short circuit currents, that is, to currents that are many times higher than the rated ones. The reaction time of the machine must be such that the wires do not have time to heat up to dangerous temperatures.
From all of the above, one important conclusion follows: the circuit breaker is designed to protect wires, cables and various electrical devices connected to the circuit from overload and short circuit. There is not a word about the person. Therefore, you should understand the main thing - the machine does not save a person from electric shock. The machine saves cables and wires.
Let's give an example. Let’s say that the lighting circuit in an apartment is protected by a 10 Ampere circuit breaker and a person, while changing a light bulb in a lamp, accidentally touched a live phase conductor and touched the grounded body of the refrigerator with the other part of his body. An electric current begins to flow through the human body, which depends on the resistance - the greater it is, the less the current. In calculations, the resistance of the human body is assumed to be 1 kOhm, which means the current will be I= U/ R=220/1000=0.22 A=220 mA . For a fatal electric shock to a person, 80–100 mA is enough, and the machine has a rated current thousands of times higher. Therefore, we repeat - the machine does not save a person from the damaging factors of electric current. Of course, a triggered machine can save someone’s life if it prevents the electrical wiring from catching fire, but it does not save a person from direct exposure to electric current.
Briefly about the “inner world” of the machine
A circuit breaker is a complex electromechanical device. Some modern models of machines are equipped with electronic units that more accurately monitor flowing currents, but in this article we will look at the device of the “classics”. The machine is shown in cross-section in the following figure.
Device
circuit breaker
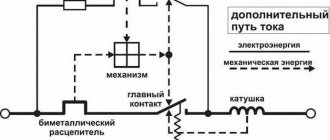
There are terminals at the top and bottom of the machine, and it is always accepted that the input is at the top and the output at the bottom. The upper terminal is rigidly connected to a fixed contact, and the lower terminal is connected to a thermal release, which is a bimetallic plate that bends when heated. The end of the bimetallic plate is connected by a flexible conductor to one of the solenoid terminals of the electromagnetic release. The other output of the solenoid is connected by a flexible conductor to a moving contact.
The release mechanism is designed in such a way that the moving contact is spring-loaded and securely fixed both in the on and off state. In addition, the springs allow switching to be carried out very quickly, which avoids severe burning of the contacts during a spark or arc discharge, which can occur precisely at the moment of shutdown.
The release mechanism can be activated in three ways:
- Turning on the machine, that is, when the moving contact is pressed against the stationary one, is possible only manually, through the control lever of the release mechanism. You can also turn off the machine manually.
- When there is an overload in the circuit, a current that exceeds the rated current passes through the bimetallic plate of the thermal release, heating it too. Under the influence of temperature, the plate bends and presses on the lever of the release mechanism, which turns off the machine. The higher the current overload, the faster the plate heats up and the faster the mechanism operates.
- If short circuit currents occur in the circuit, then the current passing through the solenoid of the electromagnetic release induces a magnetic flux capable of drawing the spring-loaded core of the solenoid inward, which, in turn, acts on the moving contact and opens the circuit. In this case, the reaction time for good machines can be thousandths of a second.
At the moment of disconnection, a spark discharge may occur between the moving contact, which ionizes the atoms of gases that make up the air. Ionized gas is a good conductor, so an electric arc can flash, the temperature of which can reach several thousand degrees. Naturally, such a thermal effect will very quickly burn out the circuit breaker if special measures are not taken.
The temperature of the electric arc can reach several thousand degrees
The machines always have a special arc chute, which is a set of copper or copper-plated steel plates that are insulated from each other. When an arc lights up, it forms a powerful magnetic field, which induces an EMF in the plates, which also forms its own magnetic field opposite in polarity. These fields interact with each other, the arc is drawn into the plates of the arc chute. The plates “shred” the arc into pieces and cool it, as a result of which it quickly goes out. When an arc burns, a large amount of gases are formed, which freely exit the machine body through a special hole located below the arc extinguishing chamber. This process may take a fraction of a second, but even this time is enough for the spark discharge or arc to “burn” the contacts a little.
Circuit breaker arcing chamber
Over time, with frequent switching on and off of machines, the contacts burn out. There were times when the contact pads of circuit breakers were made of electrical silver; there are such devices now, but they are not used in household electrical wiring. Therefore, there is no need to “click” the lever of the machine unnecessarily, since with each action there at least a spark discharge occurs, causing erosion of the contacts. Automatic machines are designed mainly to protect cables or wires, and for switching there are special devices - load switches, called switches in Russian.
Find out how to connect a difavtomat, its purpose, basic circuits, and common mistakes in a special article on our portal.
How to choose the right circuit breaker
Before installing a circuit breaker in an electrical panel, it must be selected correctly so that it matches both the cable and the nature of the load. Therefore, we will consider the main characteristics of modular machines, which are always indicated on their labeling. For a specialist, the marking says a lot, but for the “ordinary person” it means nothing. Therefore, you need to learn to read it, especially since there is nothing complicated about it.
Educational program on marking machines, selecting the right model
The figure shows typical markings for all circuit breakers. Let's look at all the points one by one and at the same time comment on which machines are needed for various purposes.
Circuit breaker marking
Trademark
The brand name is always indicated at the top of the front panel of the machine, which in other words means the manufacturer. For security devices, this is of great importance, since it is better to choose a machine from a well-known brand. These are: ABB, Legrand, Hager, Merlin Gerin, Schneider Electric, IEK, EKF. When choosing a specific model and series, it is better to consult a good (not housing office) electrician.
Rated voltage and frequency
If the machine has the inscription 220/400V 50 Hz, this means that this device can operate in both single-phase and three-phase alternating current circuits with a frequency of 50 Hz. Most machines used in household wiring have this capability.
Rated current
This is one of the main characteristics, which indicates what maximum current in amperes can flow through the machine for a long time without tripping it. It is designated In . If the current becomes 13% higher than the rated current, i.e. I= In*1.13 , then the thermal release starts working, but its response time will be more than an hour. Upon reaching I=1.45* In, the response time of the thermal release will be less than an hour and the higher the current, the shorter the response time.
The rated current of the machine must always correspond to the cross-section of the cable or wire of the circuit it protects, but not to the load power. The machine should not allow them to overheat when electric current flows, but in real life the opposite often happens.
For example, a family acquired a washing machine and, when connecting it to an existing outlet, after a while the machine in the driveway switches out, since the total load turns out to be higher than it can tolerate. An electrician from the housing office came and offered an “ingenious” solution to replace the machine with another one with a higher rated current. For example, there was a 10 A circuit breaker in the panel and it is proposed to change it to 16 A, or even 25 A, to make it “more reliable”. The machine is being changed and, to the delight of the owners, it actually stopped knocking out when the washing machine was running. And the wiring is made with aluminum wire with a cross-section of 1.5 mm2, which is far from uncommon in houses built during the USSR era.
Naturally, during peak loads the wire will overheat and its insulation will melt, but the machine will not react in any way, since its response threshold is much higher. Unfortunately, such situations are far from uncommon. And the owners will be very lucky if there is no fire, but a short circuit occurs, which will force the machine to operate.
You should understand simple rules that will help you choose the right machine that is guaranteed to protect the wiring from overheating.
- The cross-section of the cable or wire must correspond to the load.
- The rating of the circuit breaker must correspond only to the cross-section of the cable or wire, but not to the load.
The table below shows the correspondence between the cross-section of the copper cable or wire and the rated currents of the circuit breakers. In any case, it is necessary to be guided by precisely this correspondence and nothing else. No exceptions or arguments like “I’ve done this a hundred times.”
Table of correspondence between the cross-section of wires and cables and the value of the rated current of the circuit breaker. It is recommended to print and save at least for the rest of your life.
The table shows that the machine does not allow you to use all the capabilities of a cable or wire for passing electric current, but limits them. And this was done intentionally, the circuit breaker is a kind of “weak link” that will not allow the cable or wire to “strain” too much, which, from a safety point of view, is very useful.
The rated current circuit breakers are 1A, 2A, 3A, 6A, 10A, 16A, 20A, 25A, 32A, 40A, 50A, 63A.
Time-current characteristic
Before the value of the rated current in the marking of the machine there is a letter index, which reflects the time-current characteristic (VTC). It is unknown for what reason, but, from the authors’ point of view, this is not given enough attention. Let's figure out what this characteristic is.
Time-current characteristics of circuit breakers of categories B, C and D
The figure shows a graph of the dependence of the operation time of the machine on the multiplicity of the flowing current to the rated current, that is, k= I/ In . The graph is divided into three color zones: green, blue and yellow, which corresponds to the time-current characteristics B, C and D. The following conclusions can be drawn from the graph:
- When k is greater than 3 but less than 5, the machine belongs to category B.
- When k is greater than 5 but less than 10, the machine belongs to category C.
- When k is greater than 10 but less than 20, the machine belongs to category D.
What does this mean in human language? The graph shows that in any category of machines, the greater the multiplicity of the flowing current in relation to the rated current, the faster the operation will occur. Circuit breakers with VTX category B react fastest to overcurrent, followed by circuit breakers of category C, and then D. There are also circuit breakers with characteristics K and Z, but they are not used in apartment and house wiring.
It is worth noting that the graph is given for certain external conditions, namely an ambient temperature of +30°C. When the temperature rises, the machines will operate at slightly lower currents, and when the temperature decreases, on the contrary, at higher currents. This difference is not so significant, but it still exists. The operation of circuit breakers is greatly influenced by their “neighbors” on the electrical panel, which, heating up when electric current flows through them, heat both the air inside the panel and the nearby equipment. That is why experienced electricians try to choose models of electrical panels that have a lot of free space inside and, when assembling them, do not try to fill them with modular equipment “to capacity.”
The question arises: why divide circuit breakers into categories according to their performance characteristics? After all, you can simply make a device that will simply respond by turning off when the flowing current exceeds the rated one. But it's not that simple. Some types of electrical loads, when turned on, consume currents that are much higher than when they are running. For example, the electric motors of a vacuum cleaner or refrigerator compressor can consume a current that is 3-8 times the rated current at startup. If the machines react to such an excess every time, then life will turn into a living hell - every time you turn on the refrigerator, the machine in the panel vibrates. That is why thermal releases are used in automatic machines, which have a certain inertia, which allows for short-term excess current without leading to overheating of the wires. In any case, the thermal release is configured in such a way that it turns off the circuit before the cables and wires enter a dangerous mode.
Bimetallic thermal release plate
In the electrical wiring of apartments and private houses, circuit breakers from categories B and C are used. When choosing a specific model, the nature of the load should be taken into account. For active loads, that is, those that do not consume high currents when starting, you should choose machines with VTX type B. This applies to lighting and socket circuits. Reactive loads will already require machines with VTX type C. These include refrigerators, air conditioners, washing machines and dishwashers, home workshops where power tools are used.
Diagram of starting current of the heating circulation pump
Unfortunately, it is very difficult to find type B circuit breakers in electrical supply stores. This is due to the fact that there is low demand for them. The lion's share of machines sold are VTX type C. But the authors of the article strongly recommend that you spare no expense and use type B machines for active loads. Even if you have to order them and wait for some time. The fact is that by combining circuit breakers with characteristics B and C, it is possible to achieve selectivity in the operation of protection devices.
Let's give an example. Let's say an incandescent lamp in one of the lamps has burned out, but the spiral has closed. Surely everyone has encountered such a situation when, when you turn on the light, the lamp flashes and immediately goes out with a characteristic click and at the same time knocks out the machine. It’s good if the machine, which only protects the room’s lighting circuit, is triggered, but it could happen that the machine located in the access panel is knocked out. Moreover, it happens that the machine guns in the apartment panel did not react, but the entrance one did. If this happens, it means that selectivity is poorly organized in the organization of electrical wiring.
The main principle of selectivity is that the protection devices closest to the source of the problem should operate first. If for some reason they do not work, then other devices located higher in the hierarchy must respond. In the described case with a lamp, you can install a machine with VTX type B on the lighting circuit, and install a machine of category C in the driveway panel. Then, when the lamp spiral is closed, the more “fast” machine of type B will work first, while the driveway machine is “stupid.” In this case, its slower response is beneficial, since it will not turn off the entire apartment.
Rated breaking capacity
This characteristic can also be called the ultimate switching capacity (UCC). PKS shows at what maximum short circuit current the machine will still be able to open the circuit at least once (and this will most likely be the last) time. Standard PKS values are 4.5 kA, 6 kA, 10 kA. For domestic use, 4.5 kA is quite enough, but if the substation is located nearby, then it makes sense to use machines with a 6 kA PKS. Circuit breakers with PKS 10 kA are used only in industry.
Current limiting class
This characteristic has three values – 1,2 and 3, and if this marking is not present, then the machine belongs to class 1. It shows how quickly the machine will react to the appearance of short circuit currents. If a thermal release can “tactfully wait” when an overload occurs, then an electromagnetic release must act “decisively and boldly” when a short circuit occurs. The current limiting class precisely reflects the degree of “decisiveness” of the machine and its reaction time.
Graphic display of the current limiting class of the circuit breaker
Class 1 opens the circuit in one half-cycle, which is approximately 10 ms in time, class 2 - in ½ half-cycle (5-6 ms), and class 3 in 1/3 of the half-cycle (3 ms). Naturally, the higher the class, the better, but also more expensive.
Number of poles
In modern apartment or house electrical panels, modular circuit breakers are used that have 1, 2, 3 or 4 poles. Single-pole and two-pole circuit breakers are designed to protect single-phase circuits, and three- and four-pole circuit breakers are designed to protect three-phase circuits. According to the number of poles, circuit breakers occupy the number of spaces (modules) in the electrical panel. One place is 17.5 mm.
Video: How to choose circuit breakers
How to connect a machine in a panel
As noted above, modern circuit breakers used in household electrical wiring are modular equipment, which, along with other control, switching, metering and protection devices, have housings of standard sizes in length and height, and the width is always a multiple of one module (location) equal to 17 .5 mm.
All modular equipment in electrical panels is mounted on a 35 mm wide DIN rail using a latch. To install, simply snap the machine onto the rail, and then move it left or right to the desired position. And to remove it you will need a screwdriver with a straight slot, which you need to pry and pull up the spring latch.
Automatic switch on DIN rail. Back view
To install and connect a circuit breaker to an electrical panel, you will need a standard set of electrical tools:
- A set of screwdrivers, both straight and Phillips. You should pay attention to which screws and which slots are used in the terminals of the machine. There can be two options: a cross-shaped Philips type (numbered in the figure 2) or a cross-shaped Pozidriv type (numbered in the figure 3). They are designated PH or PZ, respectively.
Each slot has its own tool: a screwdriver or a bit
- Pliers of various sizes.
- Wire cutters or cable cutters.
- Insulation stripping tool - stripper.
A popular and favorite stripper model among electricians
- If stranded wires are used for connection, you will need a tool for crimping the terminals - a crimper.
Crimper from a well-known manufacturer
- Indicator screwdriver.
We will describe the process of installing and connecting a circuit breaker in an electrical panel.
| Image | Description of process steps |
| The electrical panel is completely de-energized, and measures are taken to prevent unauthorized switching on of voltage. Use an indicator screwdriver to check the absence of voltage in the panel. | |
| The machine of the selected rating snaps into place on the DIN rail. | |
| If there are empty spaces to the left and right of the machine, then it is advisable to use special limiters that prevent the equipment from moving left and right along the DIN rail. | |
| When connecting a single-pole circuit breaker, the phase from the input device or RCD (individual or group) must be supplied to the upper terminal, and the phase of the protected circuit must be supplied from the lower terminal. | |
| When connecting a two-pole circuit breaker, phase should be supplied to the upper left terminal, and zero to the right terminal. The phase of the protected circuit should “leave” from the lower left, and zero from the right. | |
| When connecting a three-pole circuit breaker, the upper terminals must be supplied with phases in the order they follow from left to right A, B, C (L1, L2, L3). Accordingly, the phases of the protected circuit must “leave” from the lower terminals in the same order. | |
| A four-pole machine is connected in the same way as a three-pole machine, only a neutral wire is added - the one on the far right. | |
| In the electrical panel, suitable wires and wires of the protected electrical circuits are laid to the corresponding terminals of the circuit breakers. Incoming ones are routed to the upper terminals, and outgoing ones to the lower ones. The only way! When laying, you should use existing bundles of wires. If necessary, the laid wires are tied to the bundles with plastic clamps. | |
| When laying wires, you should avoid sharp turns, which can cause creases. Also, do not pull the wire under tension. | |
| When the wires are laid to the corresponding terminals of the machines, their required length is measured so that the wire fits freely into the terminal. The excess ends are bitten off. | |
| A stripper removes 10 mm of insulation from the ends of the wires. If you don’t have a stripper, this can be done with a construction knife, but you should try not to cut the insulation perpendicular to the wire - this can cause further wire collapse. | |
| If stranded wires are used, they must be terminated with lugs of the NShVI type, which are crimped with a special tool - a crimper. | |
| If the circuit breaker is located next to others in the electrical panel and all of them “distribute” one phase or a phase together with zero, then it is advisable to use special comb buses, which, like circuit breakers, are one, two and three-pole. | |
| If there are no combs, you can make jumpers from the PV3 mounting wire and NShVI lugs (2), intended for crimping two wires. You cannot place two separate wires under the terminal of the machine. | |
| After checking that the installation complies with the circuit diagram of the electrical panel, the wires are placed in the previously released terminals of the machine and clamped with a screwdriver with a force of 0.8 N*m. There is no need to try to tighten it as much as possible, as this can lead to breakage of the machine body. | |
| Voltage is supplied to the electrical panel, all protection devices are turned on, an indicator screwdriver or a multimeter is used to check the presence of voltage at the input and output of the machine. | |
| The insides of the electrical panel are covered with a protective cover - plastron. A marking is placed on the circuit breaker indicating that it belongs to the protected circuit. Marking is also done on the plastron. |
Video: Circuit breakers - polarity and connection diagrams
What to do if the circuit breaker in the electrical panel has tripped?
If a circuit breaker trips during operation of the electrical wiring, there may be many reasons for this. Therefore, there is no need to rush to immediately turn it back on, but try to find out the source of the problem. In this case, you should be guided by the following:
- Any shutdown of the machine causes strong heating of its internals, especially the bimetallic plate of the thermal release and the solenoid. Before turning on the load, you need to allow a few minutes to cool down.
- While the machine is cooling down, you need to walk around the apartment or house and inspect all the sockets, switches, lamps, and powerful consumers of electricity. The smell of burnt insulation, darkening from exposure to fire, and hot plugs can tell a lot and point to the source of the problem.
- If everything is in order with selectivity in the electrical panel and only one circuit breaker has worked, protecting a specific circuit, then the task is simplified, since it is necessary to inspect the consumers of only this circuit. It is much worse when the input machine worked, and others “ignored” the problem. Then you will have to turn off all the lines protected by circuit breakers, turn on the input machine and sequentially turn on all the circuits, one at a time. After turning on any circuit, you need to give a certain waiting time and at the same time inspect all the electrical appliances that are connected to the machine.
- If, when the machines are switched on sequentially, one of them is triggered or the input machine is turned off, then the source of the problem has already been localized and the problem must be looked for in a specific circuit. This could be some kind of faulty consumer of electrical energy, a burnt-out lamp with a shorted filament, melted insulation on some section of the wiring, and much more. To find out what’s wrong, when the machine is turned off, turn off all electricity consumers in this circuit, and then turn on the machine. If it works, then the problem is in the wiring and you cannot do without the help of specialists. If not, then all consumers must be connected in series, which will help identify the faulty device.
- Disabling a machine in a particular line or input line can cause a very large load. For example, a washing machine, dishwasher, air conditioner and electric oven are turned on at the same time. The input machine may not be designed for such a load, and therefore turns off the circuit. In this case, it is necessary to divide the operation of powerful electrical appliances over time.
- Hot summer weather combined with high loads can also cause protection devices to trip.
- And the last reason is a malfunction of the circuit breaker itself. It is possible that before this it was triggered more than once by increased currents, briefly endured short-circuit currents, and repeatedly extinguished the arc. All these influences, unfortunately, do not affect the life expectancy of the machine for the better. With the plastron removed, you can inspect the inside of the shield. A faulty machine can be identified by a melted body, burnt terminals and other signs. Simply replacing the circuit breaker may solve the problem.
Clear signs that circuit breakers need to be replaced
Video: Circuit breaker - why does it trip in the heat?
Video: Circuit breaker knocks out
Conclusion
Summing up the article, the authors intend to remind readers of its main points.
- A circuit breaker is designed to protect the cable or wire, not people.
- The rated current of the machine must strictly correspond to the cross-section of the cable or wire being protected.
- In circuits with active loads, it is better to use machines with a time-current characteristic of category B, and with reactive ones, which have high starting currents, - category C.
- A proper combination of circuit breakers with VTX B and C will ensure selectivity.
- When any circuit breaker trips, you must first identify the source of the problem. If you can’t do it yourself, you should call a specialist.
Reliable and safe electrical wiring for you!
HOW MANY MACHINES CAN BE CONNECTED TO ONE RCD?
We wrote in detail about how many circuit breakers can be simultaneously connected through one Residual Current Device HERE.
In addition, be sure to read the material about why the RCD trips and how to find the fault.
If you still have questions about the design of the RCD or the principle of its operation, leave them in the comments to the article. In addition, be sure to write if you have any additions or comments, I will be grateful!
How to properly connect circuit breakers in an electrical panel
Automatic switches, also known as packets or automatic machines, are switching devices whose task is to supply current to the elements of the electrical network, and if its operation is disrupted, to automatically de-energize it. They are usually mounted in a distribution panel and allow you to protect the circuit from damage caused by excessive loads, voltage drops, and short circuits. In this material we will talk about how this equipment is classified, what are the features of its operation and how to correctly connect the machines in the electrical panel.
Classification of circuit breakers
Today, these devices are sold in a huge range. They differ from each other in the following characteristics:
- Main circuit current. It can be variable, constant or combined.
- Control method. The equipment can be operated manually or using a motor drive.
- Installation method. Devices can be plug-in, retractable or stationary.
- Type of release. These elements can be electronic, electromagnetic and thermal, as well as semiconductor.
- Body type. It can be modular, cast or open.
- Operating current indicator. Its value can range from 1.6 A to 6.3 kA.
Modern machines have a complex network protection mechanism. They have additional capabilities, which include:
- Possibility of opening an electrical circuit from a distance.
- Presence of signal contact groups.
- Automatic activation of the protective device in the event of a voltage drop to a critical value.
Step-by-step diagram for selecting a circuit breaker in the video:
Packers can have different standard sizes, and with their help you can protect electrical networks not only in apartments and private houses, but also at large facilities. These devices are produced both in Russia and abroad.
In domestic conditions, modular circuit breakers, small and lightweight, are most often used. They received the name “modular” due to their standard width, which is 1 module (1.75 cm).
In order to protect the electrical circuits of buildings, the following types of switches are installed:
- Differential.
- Automatic.
- RCD.
RCDs, as residual current devices are called for short, prevent electric shock to a person who touches the conductor, and prevent surrounding objects from igniting if there is an electricity leak, which can happen if the cable insulation is damaged.
Circuit breakers protect circuits from short circuits and allow you to turn the power on and off manually. The most advanced protective device is a differential circuit breaker. It combines the capabilities of a residual current device and a conventional circuit breaker. This package is equipped with built-in protection against too powerful electron flow. It is controlled by differential current.
In single-phase electrical networks, single-pole and double-pole circuit breakers can be installed. The choice of package is influenced by the number of wires in the electrical wiring.
Circuit breakers: design and principle of operation
Before we consider the procedure for connecting circuit breakers in an electrical panel, let’s figure out how they are designed and on what principle they are triggered.
The product includes the following elements:
- Frame.
- Control system.
- Top and bottom terminals.
- Switching device.
- Arcing chamber.
Fire-resistant plastic is used as material for the manufacture of the housing and control system. The switching device contains moving contacts as well as fixed contacts.
An arc-extinguishing chamber is installed on a pair of contacts, which are the pole of the packetizer. When the contacts break under load, an electric arc occurs, which is extinguished by the camera. The latter consists of steel plates, insulated from each other and located at the same distance. The chamber plates help cool and extinguish the electric arc that appears during malfunctions. Machines can have one, two or four pairs of contacts.
Two-pole circuit breakers have two pairs of contacts: one is movable, the other is fixed.
Such a switch is equipped with a position indicator, which makes it easy to find out whether the machine is on (red light) or off (green).
Replacement and installation cost
The price of the service in rubles depends on the type of RCD:
- For 2 poles - 350.
- For 4 poles - 450.
Installing a difavtomat costs the same.
Additional work:
- Shield rework - from 450.
- Tire installation - 100.
- Installation of DIN rail - 200.
- Dismantling of an old product - 100.
In the absence of experience, it is better to use the services of a qualified craftsman, since we are talking about the safety of residents.
Video instructions
Sources
- https://viva-el.by/stati/shema-podkluchenia-uzo
- https://220.guru/elektrooborudovanie/avtomaty-uzo/sxema-podklyucheniya-ustrojstva-zashhitnogo-otklyucheniya.html
- https://housetronic.ru/electro/podklyuchit-uzo.html
- https://remont-book.com/kak-podklyuchit-uzo-i-avtomaty/
- https://www.asutpp.ru/kak-pravilno-podklyuchit-uzo.html
- https://househill.ru/kommunikacii/electrika/zazemlenie/poshagovoe-rukovodstvo-o-tom-kak-pravilno-podklyuchit-uzo.html
[collapse]
TOP 5 RCD manufacturers
- ABB is a Swedish-Swiss company that produces high quality electrical equipment;
- Legrand is a French company, manufacturer of high-quality electrical products;
- Schneider Electric is a French company whose products are also known for their quality;
- EKF is a Russian company that produces high-quality low-voltage electrical equipment of the budget class;
- The IEK group of companies is a leading Russian manufacturer of electrical equipment in the budget category.