How to calculate cement consumption per 1 m2 (1 cubic meter, 1 m3) of brickwork
Cement consumption per 1 m2 of brick laying is a very important value that must be calculated before starting work.
Cement mortar in brickwork serves to hold individual blocks together into a single monolithic structure. The consumption of the mixture can vary within quite noticeable limits and depends on a lot of factors, starting from the recipe of the cement mortar itself and ending with the professionalism of the master. Determining how much cement is needed per 1 cubic meter of brickwork for the entire construction process is necessary in order to correctly calculate the volume of building materials. Cement belongs to the category of dry mixtures that are not stored for long.
Therefore, it is advisable to know exactly the required number of bags of the mixture in order to avoid unnecessary costs. On the other hand, if there is not enough solution, during the work you will have to go and buy more, which will require time and will stall all the work.
For brickwork, cement mortar is most often used (with or without various additives), since other mixtures do not provide the necessary characteristics of strength, reliability, and durability. Calculating cement for bricklaying usually involves determining the required volume of the mixture for 1 cubic meter of masonry.
Calculation of cement consumption for brickwork
You can find out the cement consumption per brickwork by reading the article. Here you will find information regarding the footage and how much cement composition is used per meter of masonry.
How much cement is needed for brickwork?
At the beginning of construction work, the most important role is played by the correctly planned and calculated amount of building materials and the budget required for this. This will help you save money without buying too much, and you won’t have to dramatically slow down the construction process due to the fact that there is not enough material and there is no money to buy additional ones. It is necessary to correctly calculate the cement consumption
so that the work is completed quickly and without delays.
The main step in planning a budget for construction is the correct consumption of cement. Most often, an ordinary fastening solution is used, consisting of cement of the required grade as a binder, well-cleaned sand, which acts as a filler, and ordinary water to dilute this entire mixture. How strong the brickwork will be depends on the main components of this mixture, namely the amount of sand and cement and their balanced proportions.
In some cases, to increase the mobility of the mortar or to increase its adhesive strength, additional components are added to the basic composition of the mortar, such as clay, lime, or other chemicals, which greatly simplifies the laying process.
How to find out the consumption?
It is necessary to take into account that the already mixed solution is short-lived and dries quickly. It will need to be used within a couple of hours, although all the components are stored separately for a very long time, so it is better to cook it in portions and completely use it up, rather than rush to mix everything at once.
The classic scheme for preparing the solution is quite simple; all you need is:
- Measure one part of the cement we have chosen with a bucket or kilograms.
- Add four parts of sifted and purified construction sand to the cement.
- Stir everything well and dilute with water.
Cement consumption rate per 1m2 of masonry
The rate of consumption of cement mortar per 1 m2 of brickwork directly depends on the thickness of the latter: the thicker the wall, the more material is required. For walls with a thickness of a quarter of a brick per 1 m2 of masonry you will need:
- 5 kg of cement in a solution of grade M100;
- 4 kg for brand M75;
- 2.5 kg for brand M50.
Brickwork diagram.
Cement mortar is consumed approximately the same for brickwork, about 300 kg per 1 m3 (0.25-0.3 cubic meters of mortar per 1 cubic meter of surface). A cement to sand ratio of 1:4 allows for optimal rigidity, mobility and adhesion. If other components are added to the batch, such as clay, limestone, marble, synthetic additives, etc., the ratio decreases down to 1:9. To prepare concrete, cement consumption should not exceed 500 kg per 1 m3. The exact characteristics of concrete are fixed by GOST, but it is allowed to change the proportions for the production of concrete to obtain certain characteristics of viscosity, density and drying time of concrete. To prepare a masonry batch, you will need the following tools:
- container for mixing and measuring (you can use a bucket or trough);
- mortar mixer or hammer drill with a mixer attachment;
- shovel.
Mortar consumption per 1 m² of masonry
Construction work using cement-based mortar requires the advance purchase of all components that make up the mixture.
Brick laying diagram.
Particular attention is paid to such indicators as cement consumption and its procurement, since this material cannot be procured for future use due to increased hygroscopicity and, as a result, a rapid transition to a state of unsuitability. First of all, you need to decide on the brand of material that matches your type of work, since certain types of mortars are required for certain purposes (cement-sand, slag-cement, concrete and others)
The type of brick used is determined according to the project. For example, plastic-pressed ceramic products are popular for laying walls due to their frost and moisture resistance. Hollow ceramic bricks have low thermal conductivity, but can reduce the weight of the structure by 25% and the thickness of the walls by 20-25%. Ceramic material cannot be used for stoves, exhaust pipes and chimneys. When laying the foundation, solid pressed bricks or heavy concrete blocks are used, and for external walls - silicate hollow bricks or light concrete blocks
First of all, you need to decide on the brand of material that matches your type of work, since certain types of mortars are required for certain purposes (cement-sand, slag-cement, concrete and others). The type of brick used is determined according to the project. For example, plastic-pressed ceramic products are popular for laying walls due to their frost and moisture resistance. Hollow ceramic bricks have low thermal conductivity, but can reduce the weight of the structure by 25% and the thickness of the walls by 20-25%. Ceramic material cannot be used for stoves, exhaust pipes and chimneys. When laying the foundation, solid pressed bricks or heavy concrete blocks are used, and for external walls - silicate hollow bricks or light concrete blocks.
The strength of the structure directly depends on the brand. For example, if you are making a floor screed, you need a mixture from M200 to M300, for laying walls made of bricks or foam blocks it is best to use a mixture with a hardness from M50 to M100, for foam blocks - from M50 to M100, and making a foundation requires a strength from M200 to M100. M300.
Scheme of brickwork using mortar.
Once the brand of material, mortar and type of work have been determined, it is necessary to select the appropriate brand of cement. When making a cement-sand mixture, the grade must be two to three times higher than the grade of the mortar. For example, for composition M200 you will need cement M400 or M500, and for concrete blocks it is necessary that its grade be six to eight times higher than the grade of the mixture.
Of course, the consumption of materials depends on many different factors, for example, such as: the size of the structure, the thickness of the seams between the rows, the size of the block and many others. However, the average values of consumption indicators per 1 m2 can be calculated using the tables provided.
Solution consumption per 1 m3
To find out the amount of mortar per 1 m 3 of brickwork, consider the following data. Ordinary brick has dimensions 250×120×65. There are certain standards that show how much mortar is needed per 1 m 3 of brickwork:
- 0.189 m 3 when built in half a brick (120 mm);
- 0.221 m 3 when built in one (250 mm);
- 0.234 m 3 during construction of one and a half (380 mm);
- 0.240 m 3 when built in two, (510 mm);
- 0.245 m 3 when built in two and a half, (640 mm).
It turns out that for 1 standard brick there is 0.0006305 m 3 of mortar. If we convert this into liters, then for 1 m2 with a thickness of 12 cm, there are 75 liters of the finished mixture, and when the thickness is 1.5 bricks (380 mm), the consumption increases to 115 liters.
If we talk about thickened products (modulated), then with their dimensions 250x120x88, the consumption is as follows:
- 0.160 m 3 of composition, when working in half a brick (120 mm);
- 0.20 m 3 of composition, when working alone, (250 mm);
- 0.216 m 3 of composition, when working at one and a half, (380 mm);
- 0.222 m 3 of composition, when working in two, (510 mm);
- 0.227 m 3 of composition, when working at two and a half, (640 mm).
Based on these data, it is clear how the size of the material affects the consumption of the mortar per cube of brickwork. There is a certain pattern: the larger the area, the less composition is required. Knowing this data, you can prepare the required amount of mixture for masonry. All you have to do is calculate the total footage and multiply it by the consumption per 1 m 3. Now you are prepared and can purchase materials for work. Below is a table that will help you find out the consumption of cement and additives to obtain the ideal consistency of the composition.
How much mortar is needed for 1m2 of brickwork
How much mortar is needed per 1 m2 of brickwork, how to find out. As the Russian folk proverb says: “Measure twice, cut once.” Every builder knows that before starting any work, you need to carefully calculate, study and draw up a plan. One of the reasons is to find out the required amount of consumable material, calculate how much it will cost, and purchase everything you need. If you are planning to build a house, you may be interested in the question, what is the consumption of mortar per 1 m2 of brickwork? After all, you need to buy in advance all the components for the mixture, such as sand, cement and other consumables. Please note that the quality of the finished wall is influenced by the following factors: the quality of the material and the quality of the mortar. If the wall is built incorrectly, cold bridges may occur. Therefore, it is important to prepare the solution correctly and apply the right amount.
What affects solution consumption
How much mortar is needed per 1 m2 of brickwork, mortar is the connecting link between the bricks. The solution must be of high quality, properly prepared and have a suitable consistency. One of the important points that must be taken into account when calculating is its type of composition. The most common are 4 types of solution:
- Cement-sand mixture. It consists of cement, sand and water. This composition can be called the most durable if you strictly adhere to the application technology. Otherwise, there is a danger that it will crack.
- Limestone mixture. There is no cement in its composition; it is replaced by quicklime. The mixture is quite flexible and easy to work with. But there is one drawback - rain will easily wash it out. That is why it is used only for interior work.
- Mixed solution. The composition of this mixture is combined, and combines materials from the first two types. The result is a high-quality solution that is superior to the first two.
- Composition with plasticizer. Sand of 2 mm fraction and cement are additionally mixed with a polymer additive, which increases its plasticity.
These are the most popular mixtures used in construction. An important factor is the brick itself. Its size, format, ability to absorb water and the presence of voids directly determine how much mortar will be in 1 m2 of brickwork. In general, consumption per 1 m2 is 0.2–0.25 m3. It all comes down to the fact that the thickness of the wall plays a role, be it half a brick, one, one and a half or two. The greater the thickness, the greater the consumption. The same goes for the shape of the brick. For example, if it is large, then the flow rate is reduced, if it has holes, then the flow rate increases significantly. How is the mortar for bricklaying calculated?
Amount of solution per 1 m3
How much mortar is needed per 1 m2 of bricklaying? To know the amount of mortar per 1m3 of bricklaying, let’s consider the following data. Ordinary brick has dimensions 250×120×65. There are certain standards that show how much mortar is needed per 1 m3 of brickwork:
- 0.189 m3 when built in half a brick (120 mm);
- 0.221 m3 when built in one (250 mm);
- 0.234 m3 during construction of one and a half (380 mm);
- 0.240 m3 when built in two, (510 mm);
- 0.245 m3 when built in two and a half, (640 mm).
It turns out that for 1 standard brick there is 0.0006305 m3 of mortar. If we convert this into liters, then for 1 m2 with a thickness of 12 cm, there are 75 liters of the finished mixture, and when the thickness is 1.5 bricks (380 mm), the consumption increases to 115 liters.
If we talk about thickened products, then with their dimensions 250 × 120 × 88, the consumption is as follows:
- 0.160 m3 of composition, when working in half a brick (120 mm);
- 0.20 m3 of composition, when working alone, (250 mm);
- 0.216 m3 of composition, when working at one and a half, (380 mm);
- 0.222 m3 of composition, when working in two, (510 mm);
- 0.227 m3 of composition, when operating at two and a half, (640 mm).
Based on these data, it is clear how the size of the material affects the consumption of the mortar per cube of brickwork. There is a certain pattern: the larger the area, the less composition is required. Knowing this data, you can prepare the required amount of mixture for masonry. All you have to do is calculate the total footage and multiply it by the consumption per 1 m3. Now you are prepared and can purchase materials for work. Below is a table that will help you find out the consumption of cement and additives to obtain the ideal consistency of the composition.
Calculate cement consumption for mortar
How much mortar is needed for 1 m2 of brick laying? Let’s find out the cement consumption per 1 m2 of brick laying. To do this, three conditions must be met.
- Fully calculate the volume of masonry.
- Determine the volume of the required mixture.
- Taking into account the selected ratios of the components, calculate the amount of cement.
Let's look at a simple example: you need to calculate how much cement it will take to build the outer walls of a house measuring 10x12 m. At the same time, the height of such a one-story building is 3.2 m, and standard bricks 250x120x65 are used as the material. The wall thickness was chosen to be 51 cm.
From the school curriculum we know the formula for finding volume:
- the length of the walls is multiplied by its height and thickness. In our case, these are the following indicators: (10+10+12+12) × 3.2 × 0.51 = 71.808 m3. It turns out that the required number is 71.808 m3. It's time to find out the total volume of the solution.
- Based on the data given above, the consumption of the finished mixture per 1 m3, with a wall thickness of 51 cm, is 0.240 m3.
- You can find out the total quantity by multiplying the volume of masonry by the consumption per 1 m3.
- The resulting result 71.808 must be multiplied by 0.240. Using the calculator, we get 17.233 m3. This number indicates how much cement mortar will be needed for the job. From it you only need to subtract the amount of cement.
- If the selected proportion is a component ratio of 1:3, then the following is obtained: 17.233 must be divided by 4. Now you know how much cement you need for a high-quality mortar. This number is 4.308 m3.
How much mortar is needed per 1 m2 of brickwork, the cement for the mortar was calculated in m3, but cement is sold in bags, so we convert m3 into kilograms.
Cement is packaged in bags of 25 or 50 kg, so we should convert our figure into kilograms. To do this, you need to know the density of the hardener.
- As a rule, on average this figure is 1300 kg/m3.
- Let's do the calculations: 4.308×1300 = 5600 kg.
- Now, we divide 5600 kg by 50 (the number of kg in one bag) and we get a consumption of 112 bags.
Cement consumption for bricklaying
Cement consumption per 1 m2 of brickwork directly depends on the brand of the final mortar and the initial brand of dry mixture. In any case, we recommend buying cement with a reserve, since unexpected solution costs often arise during the work. If rounding down was used during measurements or calculations, it is worth taking into account the large error in the final amount.
The consumption of cement per cubic meter of brickwork is easily calculated, but it depends on the proportion of the mortar:
- if the mixture is 1 to 3, in order to understand the amount of cement consumed, it is enough to divide 1 m3 by 4 (this is the part of the dry mixture). This turns out to be 0.25 m3 of cement per cubic meter;
- to prepare a mixture of 1 to 4, the proportion of cement will be 0.2 m3;
- if a third of lime is used as a binder, that is, the mixture turns out to be 1 part cement, 0.3 parts lime and 3 parts sand, divide 1 by 4.3 and get 0.232 m3.
The consumption of cement per cubic meter of brickwork depends on the proportion of preparation of the mortar.
Similarly, calculations of how much cement per 1 cubic meter of bricklaying are also carried out with other proportions for preparing the mixture. Cement is not calculated in cubic meters; we will have to convert the volume into weight, but this will require knowledge of the standard specific gravity (density). The brand of cement and the degree of compaction (stayed, hardened or fresh cement) have an important influence; let’s take the average number - 1300 kg/m3.
Based on the obtained value, we calculate:
- quantity of materials in a mixture of 1 to 3: 0.25 m3 * 1300 kg/m3 = 325 kg, this is how much cement is required to prepare 1 m3 of solution. To calculate how much cement is needed per 1 cubic meter of masonry, we multiply the number by the cost standard for masonry mortar. For example, we use the consumption for a single wall: 325 * 0.221 = 71.825 kg, round up to 72 kg and add an error of 75 kg. This is how much cement is needed for 1 cubic meter of masonry when using a ratio of 1 to 3;
- to prepare a 1 to 4 solution, less cement will be required. We calculate using the same algorithm: 0.2 * 1300 = 260 kg, now 260 * 0.221 = 57.46, with rounding - 58, adding the error - 60 kg of dry cement.
For convenience of calculations, the concept of a square meter of masonry is usually used. To calculate the solution consumption per 1 m2 we can use a simple formula.
Let’s not resort to calculations of the number of bricks, but rather study the legal norms and calculate the resource costs per 1 m2:
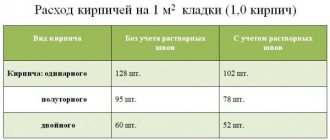
- floor bricks – 51 pcs * 0.0006305 = 0.0321 m3 of mixture per 1 m2 of masonry. We determine the amount of cement 0.0321 / 4 = 0.008025 m3 and multiply by 1300 = 10.43 kg of cement per 1 m2 of stele of 0.5 bricks;
- in brick - 102 pcs * 0.0006305 = 0.0643 m3, then 0.0643 / 4 = 0.0161 m3, now multiply by 1300 kg/m3 and get 20.9 kg of cement per 1 m2;
- 1.5 bricks - 153 pcs * 0.0006305 = 0.0965 m3 / 4 = 0.0241 m3 * 1300 kg/m3 = 31.35 kg/m2;
- in 2 bricks - 204 pcs * 0.0006305 = 0.1286 m3 / 4 = 0.03215 m3 * 1300 kg/m3 = 41.8 kg/m2.
Features of laying cinder blocks
When constructing a cinder block structure, a cement-sand mortar is usually used with the proportions of cement and sand 1:2, 1:1, 2:1, i.e. Portland cement consumption increases significantly. The need for mortar is taken from the condition that its volume is 25% of the total volume of the masonry. This calculation is valid when using the most common cheap blocks that have a sufficient range of sizes. When using high-quality foam blocks, it is better to use standard adhesives, which significantly reduces the size of the seams and demonstrates one of the advantages of such building materials.
Before starting to build a house, it is important to correctly assess the need for materials.
This is especially true for the cement component, since excess material cannot be stored for long periods of time. Calculating the need for cement for a brick structure is quite simple and takes into account the parameters of the structure, as well as the structure of the mixture used and the ratio of ingredients.
How to use the table?
Since when preparing concrete and masonry mortars it is generally accepted to operate with the volumetric characteristic “1 m3”, we calculate (reduce to 1 m3) the amount of cement for the preparation of 1 m3 of mortar with the “cement-sand” ratios of 1:3 and 1:4.
When making practical calculations of the amount of cement, novice developers make a serious mistake. They believe that if it is necessary to prepare a solution from 1 part cement and 3 parts sand, then the weight of 1 m3 should be divided by 4 and thus obtain the number of components. Actually this is not true. Since cement particles are much smaller than sand grains, it fills the voids between the sand grains, so more cement is needed. To carry out any calculation of the components of cement and sand, we will accept the following assumptions:
- One “cube” – 1000 liters;
- The volume of a bag of cement weighing 50 kg is 36 liters;
- The weight of one “liter” of cement is 50/36 = 1.4 kilograms;
Option for cement:sand ratio 1:3
To prepare the solution you will need 1 m3 of sand and 1.3 m3 of cement, which corresponds to 333 liters of cement. 333x1.4=466 kilograms of cement will be required to mix 1 m3 of masonry mortar.
Option for cement:sand ratio: 1:4
To prepare the solution, 1 m3 of sand and 1.4 m3 of cement are required, which corresponds to 250 liters of cement. 250x1.4 = 350 kg of binder will be required to mix 1 m3 of masonry mortar.
Using the obtained calculation data and the table data, as an example, we calculate the amount of cement required to mix the amount of masonry mortar per cubic meter of brickwork from a single brick of a normal format with a thickness of “1.5 bricks”.
For 1 m3 of the specified masonry, you will need to spend 0.234 m3 of solution (table). Therefore, the amount of cement solution with a ratio of 1:3 is 466x0.234=109 kg; for a ratio of 1:4 – 350x0.234=82 kg.
Using the given technology and tabular data, you can calculate the required amount of cement for masonry mortars of any ratio of components - just substitute your data.
You can also use the calculator to calculate the required amount of bricks for your home, garage or outbuilding.