Description and application of 1N-4007
Externally, 1N-4007 is a small black cylinder. It consists of a polymer resin used in the manufacture of most such elements. A semiconductor crystal is hidden inside. Its basis is monocrystalline silicon, obtained from sand through extremely high-tech technical processes.
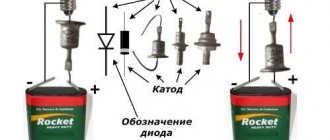
There are two electrical terminals on the sides of the diode. Their task is to conduct current from the crystal to the board into which this part is soldered. The leads are made of copper and covered with a thin layer of solder, i.e. they're cheating.
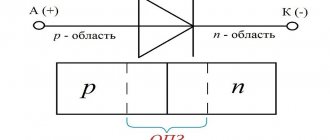
Additional Information. Diodes are designed to pass electric current in one direction, i.e. from anode (+) to cathode (-). Their hydraulic analogue is a valve. This property is inherent in this part at the level of the silicon crystal lattice from which it is produced. There are also diodes based on germanium, but at the moment they are practically not used.
Appearance
1n4007, as well as all elements of this line, have a molded body made of non-flammable plastic. In order not to think about which side of this element is which, there is a colored stripe on the casing side of the cathode output.
Installation of such diodes is allowed both vertical and horizontal - it doesn’t matter. In general, these elements are very unpretentious, which, combined with their endurance and low cost, of course, makes them truly irreplaceable.
In appearance, they are no different from other diodes, and therefore it is necessary to pay attention to what markings are applied to the body.
It is very important that such diodes are very difficult to overheat when soldering, since it has long contact legs (about 2.5 cm), which, as is known, work as a heatsink. The 1n4007 diode itself can withstand direct heating up to 250 degrees for 10 seconds.
To summarize, we can say with confidence that the diodes of this line, as well as their analogues, are a very convenient solution when assembling circuits for various power devices for both 220 and 380 volts.
The 1N4007 diode is probably the most popular of all diodes, as it is installed in the vast majority of phone chargers, smartphones and tablets. Even if you are holding a charger for a dollar and there is no stabilization or interference filters inside, it cannot do without a diode.
And in one adapter there are four such diodes and a diode bridge is assembled on them; it is used to obtain direct voltage from alternating voltage. The diode allows current to pass through itself in only one direction, cutting off one of the voltage polarities.
Read also: Grinding machine for plaster
By the way, especially cheap chargers use half-wave rectification and save three out of 4 diodes. But if the power of the power supply is more than one Watt, then it is still better to use a diode bridge, since unipolar rectification produces much larger ripples, and this mode is much more difficult for filter capacitors.
The colored ring on the 1N4007 body indicates the cathode terminal.
Since the 1N4007 is produced with leads of sufficient length, the diode can be installed both vertically and horizontally.
The 1N4007 diode is one of the representatives of a whole series of diodes 1N4001, 1N4002, 1N4003, 1N4004, 1N4005, 1N4006, 1N4007. These types of diodes differ in the value of the maximum permissible reverse voltage (the values for each type are given in the table). 1N4007 is designed for the highest voltage.
| 1N4001 | 1N4002 | 1N4003 | 1N4004 | 1N4005 | 1N4006 | 1N4007 | |
| maximum permissible reverse voltage, V | 50 | 100 | 200 | 400 | 600 | 800 | 1000 |
| maximum AC voltage (rms value), V | 35 | 70 | 140 | 280 | 420 | 560 | 700 |
Since the cost of diodes from the entire 1N4001-1N4007 series is very low, and there is practically no difference in cost between types, there is no particular point in using different types in development and increasing the range. You can install 1N4007 everywhere, even if during repairs you need to replace a diode from this series with a lower voltage.
Installation 1N-4007
1n5819 diode: characteristics
The part is installed on the board in the same way as any other two-pin elements. The algorithm of actions is as follows:
- Using special needles and a soldering iron, the mounting holes for the part are cleaned of old solder. It is even more convenient to use a tin pump.
- The diode leads are inserted into the holes according to polarity. It is indicated both on the board and on the part itself.
- The diode is pressed closely to the board. On the other side, the leads are bent. This is necessary to secure the part before soldering.
- The leads are soldered to the contact pads. Excess sections are shortened to the minimum length.
Technical characteristics of 1N-4007
It is best to look for the parameters of any part in its datasheet. Despite the low cost, the operating properties of the element are very decent. The main characteristics of the In 4007 diode include the following:
- peak reverse periodic voltage – 1000 V;
- maximum rms voltage – 700 V;
- permissible current in the forward direction – 1 A;
- peak forward current (one pulse 8.3 ms) – up to 30 A.
Diode 1n4007 characteristics
What is a diode - operating principle and device
From the datasheet it is clear that all diodes in this line have the same current, but different voltages. For example, the 1N4001 diode has the following characteristics: 35 V / 1 A.
Important! When selecting a diode (and also a capacitor), you should take into account not the effective voltage, but the peak voltage. A voltmeter connected to the outlet shows 220 V. This is the current value. Peak – approximately equal to 310 V. Upeak = 1.41*Uday = 1.41*220 = 310.2.
Specifications
The technical parameters of 1n4007 allow us to speak of it as a specialized rectifier diode designed for high alternating voltage networks with an operating frequency of up to 60 Hz. The maximum permissible operating values for the device are given in the datasheet taking this feature into account.
Limit parameters
Let's consider the main maximum permissible characteristics for 1n4007:
- peak reverse pulse voltage (VRRM) - up to 1000 V;
- maximum forward rectified current (IO) - up to 1 A;
- operating temperature range (TJ) from - 65 to + 175°C.
They are presented in the datasheet taking into account the ambient temperature (TA) not exceeding +25°C (if there is no other data).
It is worth considering that the current in the capacitive load circuit should be 20% lower than for inductive and resistive loads. This is one of the properties of the device in question, which determines its operating mode.
Electrical parameters
The 1n4007 diode is characterized by high overload capacity and low junction voltage drop (VF) - up to 1.1 V (with IO up to 1A). Thus, the maximum instantaneous pulse current (IFSM), with a duration of 8.3 seconds, can reach 30 A.
Typical junction capacitance (CT) does not exceed 15 pF. Its value is determined at a frequency of 1 MHz and a constant voltage of 4 V. In theory, such an operating speed is unacceptable for rectifier diodes, therefore their use in high-frequency circuits is not regulated.
The leakage current does not exceed 5 µA. But with an increase in ambient temperature (TA), especially at more than +75 °C, it can increase to 50 μA. At the same time, all the indicators declared by the manufacturers are deteriorating. Therefore, to achieve efficient operation, it is necessary to maintain the standard 30% margin in parameters. It is also desirable to organize cooling, for example, using a special non-conducting thermal compound.
Pinout 1N-4007
Schottky diode
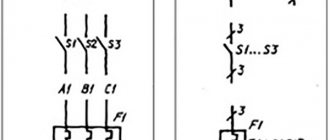
She is also a pinout. Indicates pin locations. Any diode has two of them. They are called anode and cathode. Roughly speaking, they can be called plus and minus, respectively. There is a ring strip on the body of this electronic component. It is located on the side of the cathode terminal.
There are two types of diode designations on the board. They also contain stripes. Their task is to show how to correctly install the element. The correspondence between the stripes on the real part and on the board is easy to remember from the picture below.
Diode strip
Diode Dimensions
The dimensions of the parts are especially important for designers and repairmen, because each element has its own standardized footprint on the board. 1N-4007 is available in DO-41 package. Its dimensions can be found in the datasheet for this part. At the same time, the manufacturer does not know in advance in which country its products will be sold. Therefore, dimensions are written in both inches and millimeters (mm in parentheses). Some sizes are represented by two numbers written as a fraction. They indicate the upper and lower tolerance limits.
Diode Dimensions
Diode parameters
The 1N4007 diode is a planar silicon diode with parameters standard for medium-power voltage rectifiers operating at frequencies up to 1000 Hz. In some descriptions there may be incorrect designations like in4007. Available in a DO-41 plastic case, with tinned wire axial leads, for through installation into printed circuit board holes (THT). The DO-35 and A-405 versions differ slightly in size. Surface mount (SMD) products are manufactured in DO-214 (SMA) package. Appearance In most cases, the DO-41 case is painted with abrasion-resistant paint with the full name of the diode - 1N400X.
The marking of SMD components, on which it is impossible to place the full name, has several options determined by the device manufacturer: S7, M7, A7 and others. The number here corresponds to the last one in the full designation. The negative terminal (cathode) is always indicated by a white or gray stripe. There are no special installation requirements; soldering of leads for DO-41 is allowed at temperatures up to 260 °C, for no more than 10 seconds, at a distance of 9.5 mm from the housing. Operating and limiting parameters For 1N4007, characteristics are measured at an ambient temperature of 25 ° C, unless otherwise specified.
The 1N4007 diode is one of the representatives of a whole series of diodes 1N4001, 1N4002, 1N4003, 1N4004, 1N4005, 1N4006, 1N4007. These types of diodes differ in the value of the maximum permissible reverse voltage (the values for each type are given in the table). 1N4007 is designed for the highest voltage. Comparative characteristics are presented in the table below:
Table of comparative characteristics of the 1N4007 diode and others
Material on the topic: What is a capacitor
The device is switched on using a half-wave rectifier circuit, frequency – 60 Hz, a resistive or inductive load is used. 1n5819 diode: characteristics Characteristics:
- Peak and constant limit reverse voltage – 1000 V;
- Maximum average (RMS) alternating voltage – 700 V;
- Maximum average rectified current – 1.0 A at 75 °C;
- Peak forward current during one half-cycle – 30 A;
- Voltage drop at current 1 A – 1.0 V;
- Thermal resistance crystal - case - 25 oC/W;
- Typical junction capacitance is 15 pF for a frequency of 1 MHz;
- Operating temperature – from -55 to +155 оС.
It will be interesting➡ What is the Gunn effect and what do diodes have to do with it
Other diodes in this line differ only in the values of permissible reverse voltages; they are indicated by the last digit in the marking - from 50 to 800 volts. Important to consider! The limiting value of the forward current depends on the temperature of the case (1 watt of power causes an increase of 25 ° C); in critical designs it is recommended to provide sufficient heat dissipation; in some cases, board pads can be used. Dependence of current on temperature Application features The characteristics of the 1N4007 diode determine the areas of its use - these are AC voltage rectifiers with a frequency of 50/60 Hz. For a 220 volt network rectifier, 1N4007, 05, 06 are used.
In low-power, low-voltage devices (transformer power supplies), the 1N4001 diode can be used with standard output voltages of 12, 24, 36 volts. They do not work at frequencies above 1 kHz: for example, installing a switching power supply in the output stage will lead to unpredictable consequences, including failure of the entire structure. In4007 rectifier diodes do not have unique properties and can be replaced by any with similar parameters, produced in huge quantities by all manufacturers. Domestic rectifier diodes KD243 are complete analogs, like KD208A, KD212. The only difficulty when replacing with Russian products may arise when determining the type - traditionally, domestic manufacturers mark their products with multi-colored stripes or dots, and the information contained in them can only be deciphered using reference books.
Diode 1n4007.
The 1N4007 diode is probably the most popular of all diodes, as it is installed in the vast majority of phone chargers, smartphones and tablets. Even if you are holding a charger for a dollar and there is no stabilization or interference filters inside, it cannot do without a diode. And in one adapter there are four such diodes and a diode bridge is assembled on them; it is used to obtain direct voltage from alternating voltage. The diode allows current to pass through itself in only one direction, cutting off one of the voltage polarities.
Packaging of diodes.
By the way, especially cheap chargers use half-wave rectification and save three out of 4 diodes. But if the power of the power supply is more than one Watt, then it is still better to use a diode bridge, since unipolar rectification produces much larger ripples, and this mode is much more difficult for filter capacitors.
The colored ring on the 1N4007 body indicates the cathode terminal. Since the 1N4007 is produced with leads of sufficient length, the diode can be installed both vertically and horizontally. The 1N4007 diode is one of the representatives of a whole series of diodes 1N4001, 1N4002, 1N4003, 1N4004, 1N4005, 1N4006, 1N4007. These types of diodes differ in the value of the maximum permissible reverse voltage (the values for each type are given in the table). 1N4007 is designed for the highest voltage.
Since the cost of diodes from the entire 1N4001-1N4007 series is very low, and there is practically no difference in cost between types, there is no particular point in using different types in development and increasing the range. You can install 1N4007 everywhere, even if during repairs you need to replace a diode from this series with a lower voltage.
It will be interesting➡ What is addressable LED strip
Diode marking
The body alone is not enough to identify the part. Therefore, it is customary to use short labeling. In the case of diodes from the 1 N 400X line, the designations on the case indicate the following:
- series name from 1N-001 to the most powerful of the line 1N-4007;
- electronic component manufacturer code;
- date of release of the part indicating the month and year.
Letters on a diode
The diode in question is also available in a surface mount package (SMD). Such parts are even smaller in size, so their markings are simplified to two characters.
Correspondence between conventional and SMD diodes
Diode marking in4007
Let's start with the breakdown for parts in the DO-41 case. Variants of symbols applied to it are shown in the figure.
Significant Labeling Elements
Explanation:
- Model name series 1N4001-4007.
- Graphic or alphabetic or alphanumeric code of the manufacturer of the radio component.
- Production date in month/year format (last two digits are given).
Since the SMD case is small in size, if you put the full model name on it, it will be difficult to recognize the inscription with the naked eye. Therefore, the name is encoded in accordance with the table.
Marking table for 1N400x series SMD diodes.
| M1 | M2 | M3 | M4 | M5 | M6 | M7 |
| 1N4001 | !N4002 | 1N4003 | 1N4004 | 1N4005 | 1N4006 | 1N4007 |
Replacing component 4007
It is better to replace any parts with the same ones. If you don’t have the necessary diodes at hand, you can look for them in phone chargers, various power supplies, energy-saving and LED light bulbs, children’s toys or control units for New Year’s garlands. Analogs of the 1N4007 diode are selected taking into account the characteristics.
Domestic analogues
One of the most suitable replacement options is the Russian component KD258D. It has the same reverse voltage of 1000 V as the 4007. At the same time, its forward current is 3 A, which is three times higher than the component it is replacing. Attention should be paid to the temperature. 1N-4007 is capable of operating at 150 C, and KD258D can withstand only 85.
Foreign analogues 1N-4007
Imported manufacturers boast a wider list of parts suitable for replacing a faulty diode. For example, 1N-1236 has similar characteristics. Its maximum voltage is slightly inferior to 4007 and is 800 V, and the forward current exceeds 1.6 A. 1N-1925 will be much more powerful - 800 V / 4 A. If the operating voltage is fundamental, then 1N-2193 - 1000 V / 3 A will do.
Analogs 1N4007
Of course, such a popular diode could not be ignored by global manufacturers of semiconductor devices and released their complete analogues:
- Motorola - HEPR0056RT;
- Philips - BYW43;
- Diotec Semiconductor - 10D4, 1N2070, 1N3549;
- Thomson - BY156, BYW27-1000;
- domestic analogue - KD258D.
30 thoughts on “Diode 1N4007 characteristics”
For the 1N4001 - 1N4007 series, specifications are in the datasheet.
Does anyone know the limiting operating frequency of 1N40001? I am interested in the operation of these diodes in ULF (for example, in Shushurin’s ULF in place of D223B).
I doubt that the 1N4001 is suitable for operation at audio frequencies. It is designed for 50 Hz (60 Hz). There is another, also widely used diode: 1N4148. This one might be suitable, it also has a domestic analogue KD522B.
In cases where the operating frequency of the diodes is not explicitly stated, look at the junction capacitance and the diode turn-off time. If the capacitance is more than 5 picofarads, and the turn-off time is more than 100 nanoseconds, then it has nothing to do in pulse, high-frequency and audio circuits, except perhaps as a rectifier or reference voltage source. If the capacitance and time are not indicated in the datasheet, then these parameters are not regulated at all and the diode should not be used in ULF signal circuits. This also applies to D223. In its place it would be better to put KD522 or 1N4148. Their speed characteristics are orders of magnitude better than those of the D223 and 1N4007, and in terms of maximum currents and voltages they are quite suitable for use in the circuit of the mentioned amplifier. Moreover, finding them is not a problem anywhere; diodes are very common.
D223 is used here as a stabistor. It has a forward breakdown voltage of about 2.5V.
A couple of additions: - the most common, after all, is 1N4004, since it is designed to operate on a 220V power supply, and manufacturers of chargers and other inexpensive equipment count every cent; — the maximum current is indicated for constant voltage, and in the bridge two arms work alternately, so they can withstand 2-3 times more; — compound is different from compound, epoxy resin (the most common) will only worsen heat transfer, it’s better to leave it in the air, or fill it with a special non-conductive thermal compound.
Read also: Carbide cutters for metal
I readily believe that in a bridge connection the diodes can withstand a current 2 times greater than that indicated in the datasheet. But 3 times? How? However, you should not blindly trust imported datasheets for rectifier diodes in the place where the maximum values of forward currents are indicated. As a rule, an attempt to force a 1N40xx series diode to operate within the parameters specified in the documentation leads to its failure long before the deadline specified in the same documentation. The cases are too small and the cross-section of the leads is too small, and as a result, worse heat dissipation from the semiconductor. It is not for nothing that domestic rectifier CDs were made with leads of a much larger diameter at the same declared operating currents, and in larger packages.
So currents, or rather their values, are different: peak, effective, etc. I indicated a simplified idea of the choice, nothing more. The load is such and such, yeah - these are suitable, so as not to count. But it may have sounded like a call to use it in marginal operating conditions, but I did not call for this. Correction: use semiconductor devices with a 30% margin in all respects! About datasheets: you can and should trust those that are supplied in the box along with the parts. And then there are many analogues that are not quite similar. I won’t say anything about our CDs, I don’t want to talk about sad things.
I have 20% of the reverse voltage reserve left in my memory for the domestic element base. It is surprising that for foreign semiconductors there is no need to remember such a reserve, and the repeatability of their characteristics is many times better than in products of the domestic semiconductor industry.
Everything is better there, definitely many times better, and sometimes even an order of magnitude better. No offense to the domestic industry, but at the border of the 80s and 90s it fell behind forever, and not for some years. Even then, it was necessary to purchase machines abroad, although this was hushed up for patriotic reasons, because ours not only could not cope with the increasing tasks of automation, but also could not get closer to them. And the decaying West... I had the opportunity to service such lines and visit where they were produced, so I know what I’m talking about.
I'm surprised I didn't notice this comment earlier. I'll repeat it again! Compared to domestic diodes, foreign analogues must be taken with a significantly larger margin in currents and voltages. In the datasheets everything is indicated for the most extreme modes. The bourgeoisie saves on everything they can and on what they should never save on.
Cheap power supplies also include full-wave rectifiers. In this case, the Chinese save two rather than three diodes.