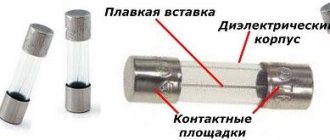
To protect the vehicle's electrical circuits from overloads, fusible or reusable inserts located in wiring boxes are used. There are different types of fuses for cars, differing in installation method and technical characteristics. Before carrying out repairs, it is necessary to open the junction box and find out the type and rating of the failed protective element.
What are fuses used in a car?
Cars are equipped with an on-board electrical network designed for 12 V or 24 V. Electrical wiring harnesses consist of individual wires with colored insulation, which allows you to determine the purpose of the cable. Copper conductors are designed to connect consumers with maximum permissible power. In the event of a short circuit, the metal overheats with melting or fire of the wiring and machine.
Fuses do not allow an uncontrolled increase in current strength and prevent the occurrence of emergency or fire hazardous situations.
Basic modifications of fuses
The main series of fuses are PN2, NPN2, PRS and PPN. First of all, these are fuses that are used in electrical equipment of industrial installations and in electrical networks and take on all overloads and short circuits. They are designed for an operating voltage of 220-380 volts and are placed on insulators in special holders that are supplied with the device itself. These devices are designed for continuous operation in a horizontal or vertical operating position.
Design and classification of fuses
To protect the electrical wiring of cars or trucks, fuses are used:
- cylindrical type, equipped with a plastic or ceramic body;
- knife blades with a plastic casing and rectangular contacts;
- bimetallic, belonging to the reusable category.
A number of automotive manufacturers use tape elements to protect circuits under high load. The plates are attached to the contacts with screws or nuts; the fuse rating is marked on the front of the part. Tape strips are used in generator circuits or in power lines for powerful consumers (current up to 110 A-140 A). To protect the box from the molten metal generated during operation, a plastic cover is placed on the plate.
Since the beginning of the 2000s. Cars began to use cassette elements equipped with a plastic housing with guide recesses.
The upper part is closed with a transparent lid indicating the denomination. There are fuses in micro-10, micro-14 and mini-14 formats that can withstand currents from 15 A to 80 A. On some cars, there are cassette clip inserts rated 25 A or 30 A.
Cylindrical modifications
The cylindrical protective element consists of a plastic body, metal caps at the ends and a connecting strip, which is destroyed when the current increases above the nominal value. Fuses are installed in blocks with spring contacts; the industry produces several types of elements that differ in permissible load.
Cylindrical inserts are used on domestic cars in 2021 (for example Lada 4×4 FL), foreign manufacturers began to switch to knife bars in the second half of the 80s.
On foreign cars and domestic cars there are inserts with a ceramic body that can withstand elevated temperatures.
The products have a size of 6x25 mm (according to DIN 75581/1 standard) and are labeled as Bosch Torpedo Fuse or Bussman GBC Fuse. Inserts with a glass body can be installed in radio receivers, allowing you to see the condition of the connecting thread. The rating rarely exceeds 5 A; at the ends of the transparent tube there are metal cups to which a jumper is soldered.
Knife guards
The classic knife insert consists of a body made of heat-resistant transparent plastic with pigment, and metal contacts. There is a jumper inside the casing, which burns out when a current exceeds the rated value. The element is installed into the block manually; the legs have bevels to facilitate installation. For removal, use plastic pliers, stored in a separate slot in a safety box (the location depends on the model and manufacturer of the car).
International standards regulate the color marking of inserts, which makes it possible to determine the denomination. For example, yellow-orange plastic is used for strips designed for a current of 5 A, and green elements can withstand up to 30 A.
In addition to standard fuses, products are produced in maxi and mini formats, differing in the sizes of housings and contact plates.
Thermal varieties
Bimetallic protective inserts consist of a housing, a spring contact and metal legs. When a current passes that exceeds the permissible (nominal) threshold, the fuse trips, cutting off the power supply. Opening occurs due to overheating of the contact plate or activation of electromagnetic protection. The car owner needs to eliminate the cause of the short circuit, and then return the fuse to working condition by pressing the button or lever located on the body.
PTC or traditional fuse?
It goes without saying that PTC fuses are highly preferred in systems that experience frequent overcurrent (the meaning of "frequent" depends on your point of view: and once a year can be considered frequent if replacing the fuse would be extremely inconvenient). In fact, you may wonder why anyone would choose a traditional fuse over a PTC fuse. Well, it turns out that PTC fuses have some disadvantages:
- They have higher resistance during normal operation.
- A tripped PTC is not an open circuit; it is simply a component with enough resistance to significantly limit the flow of current. In some applications this may not be desirable.
- PTC can hide the occurrence of overcurrent events. If you need to replace a fuse, you know what happened. If you use a PTC and change something in the circuit and remove the over-current condition, the PTC can naturally cool down and return to its low-resistance state. Or someone in the lab might see that the system is not working properly and power reset it without investigating the actual cause of the failure.
- PTCs are more sensitive to changes in ambient temperature. This is shown in the following graph; curve, o, refers to PTC, and curves, o and "B" refer to traditional fuses.
Relative change in current rating of fuses as a function of ambient temperature
Other information that can be learned from this graph is that the form factor of a traditional fuse can affect its susceptibility to changes in ambient temperature. For example, thin film fuses (corresponding to curve A) are much more sensitive to ambient temperature than terminal cartridge fuses (corresponding to curve B).
Comparison of automotive fuse sizes
Dimensions and features of the main types of fuses for cars and trucks:
- The strip jumper has 2 mounting holes with a diameter of 5.5 mm to 6.5 mm and a total length of 42 mm. The distance between their centers is 30 mm.
- Classic cylindrical fuses have a length of 25.5 mm and a diameter of 6.5 mm. The metal tips are made in the form of a cone with a right angle at the apex.
- Micro (or Mini low profile) format knife elements are equipped with legs 0.8 mm thick and 9 mm long. The width of the plastic case is 10.9 mm and the thickness is 3.8 mm.
- Mini standard fuses are distinguished by a case width increased to 11.4 mm and a thickness of 4 mm. Total height (with contacts) no more than 16.7 mm.
- The standard format element (or Norma, Regular, Standart) is equipped with a body with a thickness increased to 5.5 mm and a length of 19.5 mm. The contacts are 5.1 mm wide, which does not allow the strip to be installed in micro or mini fuse slots.
- Maxi fuses are 30.2 mm long and 9.2 mm thick; metal contacts 7.8 mm wide and 12.3 mm long are used for connection.
- The dimensions of mini or clip car cassette inserts are not regulated by standards.
PPN fuses
Fuses PPN-33, PPN-35, PPN-37, PPN-39Fuses of the PPN series (PPN-33, PPN-35, PPN-37, PPN-39) - a modern series that complies with the international fuse standard (NH) covers all types of designs provided for by technical specifications and allows consumers the opportunity to select products depending on conditions of use.
Compliance with international standards allows the use of PPN fuses instead of analogues of imported and domestic production. A wide range of rated currents allows you to make the optimal choice of fuse in accordance with the parameters of the protected circuit. Design of PPN fuses The fuse housings are made of steatite, which ensures high breaking capacity. Innovative technology for filling fuses with filler (highly purified quartz sand is used as filler) makes it possible to achieve dense filling, which ensures effective extinguishing of the electric arc inside the fuse when it is triggered. Depending on the order, fuses are supplied without auxiliary (free) contacts or with auxiliary (free) contacts. MI ZV microswitches are used as auxiliary contacts: Rated current of auxiliary contacts 2 A. Rated circuit voltage 220 V AC, frequency 50 and 60 Hz. Structure of the symbol for PPN fuses PPN-ХХ-ХХ-ХХ-ХХ
- fuse series;
PPN
fuse filled;
XX
- rated current
33
- 160A,
35
- 250A,
37
- 400A,
39
- 630A;
X
- installation method and type of connection of conductors to the fuse terminals:
2
- on its own insulating base,
5
- on the insulating base of the component device,
7
- on the conductors of the component device;
X
- presence of a trigger indicator, striker and free contacts:
0
- without trigger indicator, without striker, without free contacts,
1
- with trigger indicator, with free contacts,
3
- with trigger indicator, without striker, without free contacts;
XX
- degree of protection - IPOO;
XX
- climatic version and placement category (UHL3, T3, UHL2).
Technical data of PPN fuses
| Fuse type | Rated current of fuse link, In, A | Rated voltage, Up | Rated breaking capacity |
| PPN-33, size 00С | 2,4,6,10,12,16,25,32,40,50,63,80,100 | — 220V ~ 400V | 100 kA |
| PPN-33, size 00, 0 | 2,4,6,10,12,16,25,32,40,50,63,80,100,125,160 | ||
| PPN-35, size 1 | 2,4,6,10,12,16,25,32,40,50,63,80,100,125,160,200,250 | ||
| PPN-37, size 2 | 40,50,63,80,100,125,160,200,250,315,400 | ||
| PPN-39, size 3 | 100,125,160,200,250,315,400 | ||
| PPN-39, size 3 | 500,630 | — 440V ~500V | |
| PPN-41, size 4 | 500,630 | 50 kA | |
| PPN-41, size 4 | 800,1000 | ||
| PPN-41, size 4 | 1250,1500,1600 | ||
| PPN-41, size 4a | 800,1000,1250,1500,1600 |
RATED PARAMETERS OF PPN FUSES WITH AM CHARACTERISTICS
| Rated voltage, Up | – 220V ~ 440V / – 440V ~ 550V |
| Rated frequency | 50 Hz |
| Standard current range | From 2A to 630A |
| Rated breaking capacity | 50 kA |
The price of PN-2 fuses is from 30 rubles. Relay rev 812.
The best fuse manufacturers
Automotive fuses are manufactured in accordance with the international standard ISO 8820-1-2014, which prescribes:
- Maintaining normal operation of consumers, the voltage drop inside the element should not affect the devices.
- The jumper should burn out in 3-100 seconds when applying a current strength exceeding the rated value by 35%.
The list of the best manufacturers includes products from the following companies:
- Russian AVAR, supplying sets of elements to the spare parts market. Tests have shown that the jumper burns out when a current exceeds the rated value by 35%, after 3.5-5 seconds.
- Italian MTA, which uses heat-resistant plastic in the manufacture of inserts. The disadvantages include the oversized cross-section of the connecting jumper, which melts when the load is exceeded in 20-30 seconds (data for a 20 A fuse).
- Chinese Nord Yada, which uses bright transparent plastic for casting cases. When overloaded, the insert burns out in 2-7 seconds, providing protection for electrical wires and consumers.
- Czech Tesla, which supplies products to the assembly lines of automobile factories in Europe. The fuses meet the requirements of the concerns and can withstand an overload of 35% for 11-26 seconds (depending on the rating and batch).
Fuse types
Depending on their purpose, fuses are manufactured in various types.
Low current . They are used in circuits designed for low current consumption - up to 6A. This is perhaps the most common type of fuses that are often found in household electrical appliances. There are different standard sizes, indicating the outer diameter x length (3×15, 4×15, 5×20, 6×32, 7×15, 10×30).
This group also includes thermal fuses.
Fork . This type of fuses are widely used in cars. They differ in the size and shape of the case - Mini - H=16 mm, Standard - H=19 mm, Maxi - H= 34mm. Depending on the rated current value, the housings have different color markings.
Cork . They are used both in industrial equipment and in the residential sector. Designed for rated current up to 63A. In their design they are almost identical to low-current ones, only they have a ceramic body rather than glass. The base for such fuses is either NEOZED type threaded sockets or MINIZED type disconnectors with a drawer tray.
Knife . They are used in power circuits of electrical installations up to 1000V. Rated for current up to 1250A. The body of blade fuses is filled with a special filler to extinguish the electric arc, which is usually quartz sand. Depending on the design, they may have a visual indicator of operation and a mechanism for remote signaling of operation.
Quartz and Gas-generating . Used in high-voltage networks.
Recommendations for selection
Before purchasing a set of protective strips, you should study the information provided on the packaging. If the container does not contain information about the manufacturer, it is recommended not to purchase it. Small companies use low-quality plastic, which is destroyed by temperature changes.
The cross-section or material of the metal jumpers may not meet the requirements; in the event of an emergency, the fuse will not break the circuit or will ignite.
It is recommended to purchase inserts with transparent bodies. A number of manufacturers use matte plastic, which does not allow one to see the condition of the jumper when viewed from the side. To check, you need to look into the control window made in the upper plane of the case. You should buy fuses in large stores; in small retail outlets there is a high risk of purchasing counterfeit products.
Why is it important not to mix up fuses?
If the fuse fails (for example, it blows due to an accidental short circuit), then it is necessary to install an element with a rating that does not exceed the factory value. It is prohibited to use paper clips, pieces of foil or inserts designed for high current strength. In the event of a consumer malfunction, the load on the electrical wiring will increase, which will lead to a fire in the vehicle. Information about the ratings is indicated on the cover of the safety block, the insert body (applies to the knife type) or next to the socket for installing the element.
You should not use strips designed for a lower current, since when the consumer is turned on, the jumper will melt and cannot withstand the load. If, after installing a fuse that matches the rating, the circuit fails again, the circuit should be checked. The cause of the defect may be a short circuit inside the equipment or damage to the cable insulation, leading to contact of the core with the car body. Do not operate a machine with faulty electrical wiring due to the risk of fire.
Fuse operation
Most often, protection is carried out using fuses that protect electrical installations from short circuits. Each of them consists of a main element in the form of a fuse link. For its manufacture, zinc or tinned copper is used. At high currents, it burns out and the electrical circuit breaks.
The fuse link configuration is a wire or shaped flat strip placed in an insulating tube. Porcelain, glass and other dielectric materials are used for insulation. Thanks to this design, in addition to electrical safety, fire safety is also ensured.
Dry quartz sand or chalk can be poured inside fuses that protect against high currents. With their help, the electric arc is extinguished and cooled very quickly.