Modern electrical wiring is carried out according to a three-wire circuit, with protective grounding. And if a phase wire can be found in a three-core cable with a regular indicator screwdriver, then in order to distinguish zero from grounding it is necessary to use additional devices.
Therefore, some “experts” do not pay attention to which wire is connected to the neutral and which to the ground. This article discusses the question of whether such a connection diagram is acceptable and what will happen if you connect ground instead of zero.
Why do you need zero in the electrical network?
Power supply to modern residential areas and industrial enterprises is carried out using the TN system, or with a solidly grounded neutral. This means that the secondary windings of the step-down transformer are connected in a “star” configuration, the middle point of which is connected to the substation ground loop without interruption.
From the transformer substation to consumers, electricity is supplied through four wires - three phase wires L1, L2, L3 and one zero N. To connect a household electrical appliance, two wires are needed - phase and zero, or neutral.
In a TN power supply system, the neutral conductor performs two functions:
- In a single-phase network. For electric current to flow, the circuit must be closed. Relatively speaking, voltage is supplied to electrical appliances through phase wires, and the neutral serves to close the electrical circuit.
- In a three-phase power supply system. In this network, thanks to the phase shift, three electrical appliances of the same power can operate without a neutral, and three-phase electric motors are connected in this way. In this network, the neutral conductor does not serve to supply power, but to flow an equalizing current that appears when the load is unevenly distributed across phases and prevents voltage fluctuations when power consumption changes.
| Information! In some types of electrical cables with a cross-section of more than 4 mm², the neutral core is made of thinner wire. |
Why is grounding needed?
In a normal situation, no current flows through the grounding conductor; it is used only in the event of an emergency. Contact of high voltage with the body of an electrical appliance and subsequent touching of it is dangerous to human life, therefore, according to the PUE clause 1.7.32-33, it is recommended to connect all metal parts to the ground loop with a separate wire or using the appropriate terminal in the socket.
In this case, if the insulation between the live parts and the grounded body is broken, a short circuit appears in the network and the current in the phase wire increases sharply, which leads to the protection being triggered.
If a short circuit to the body of an electrical appliance occurs through some resistance, then the flowing current may not be enough to trip the circuit breaker. The role of grounding in this case is to reduce the touch voltage to a safe value, thereby reducing the potential difference between a person and damaged equipment. The smaller the potential difference, the smaller the current flowing through a person.
How to distinguish zero from grounding
In order to properly connect these wires, it is necessary to determine which of them is neutral and which is ground. There are various ways to distinguish zero from ground:
- Color coding. In electrical wiring made in accordance with GOST 31947-2012, the color of the wire sheath is determined by its purpose. The neutral is blue or light blue in color, the ground is painted with longitudinal yellow and green stripes.
- Using an RCD or automatic circuit breaker installed in the electrical panel. After identifying the phase conductor using an indicator screwdriver, an electrical appliance or lamp with a power of more than 10 W is connected to it and one of the remaining ones. If the protection does not operate, it means that the neutral conductor was selected. Otherwise it is ground.
- Tester or voltmeter. The electrical wiring in the panel is disconnected from the ground loop, after which one of the devices detects two wires between which there is a voltage of 220V. The remaining conductor is ground.
Differential current (RCD, difavtomat)
Another option for distinguishing zero from grounding involves the presence of differential protection in the panel with a setting of 10-30 mA. These devices compare the current flowing through the neutral and phase wires and turn off if the equality is violated.
To search for a grounding conductor, an electrical appliance, for example, a lamp with a power of more than 10 W, must be connected to the cable being tested. If the protection is triggered when turned on, it means that grounding is used instead of the neutral wire.
| Important! Before starting work, you must check the serviceability of the RCD by pressing the “TEST” button. |
What happens if you connect ground instead of zero in the socket?
The voltage at the socket terminals does not depend on which conductors are connected to them - L - N or L - PE. However, if installed incorrectly, the following may occur:
- False tripping of differential protection. RCDs and automatic circuit breakers operate on the principle of comparing the magnitude of current in the phase and neutral wires. If a person touches live parts or the insulation is broken, a leakage current appears, violating the equality, which leads to the operation of the protection. When used instead of a grounding neutral, current does not flow through it, unlike the phase wire, which leads to an emergency shutdown of the RCD or differential circuit breaker.
- Electric shock hazard. If one of the electrical appliances is connected incorrectly, and the remaining devices are connected to the grounding loop, then if the grounding conductor breaks, the housings of these devices will be connected to the phase conductor through the incorrectly connected device. Touching these parts will result in a live person being exposed to voltage.
- Accelerated destruction of the ground loop. The contour parts are made of carbon steel and are located in the ground. The constant flow of electric current through them leads to the appearance of an electrocorrosive effect and accelerated destruction of grounding conductors.
What is and how to do zeroing
WITH
With the advent of electricity in everyday life, the question of its safe use arose.
Let's see how to solve this important problem, let's figure out: what grounding is, how grounding works, how to make grounding
in a private house with your own hands.
And besides, is it possible to use grounding instead of grounding?
1.
What, how and where it comes from.
2.
Grounding in the apartment.
3.
Residual current device.
4.
Zeroing.
5.
Let's consider a couple of situations.
6.
In conclusion, about zeroing.
What, how and where does it come from?
It is known that electricity is produced by power plants. From them, an electric current with a voltage of tens and hundreds of thousands of volts travels through three phase wires to the consumer.
The voltage is so high because, according to the laws of physics, the higher the voltage, the lower the losses during transmission over long distances.
Then step-down transformer substations convert the high voltage into a much lower (but still dangerous) one, and it will come through wires or underground cables into our home.
The current must come to the electrical appliance, do useful work and leave. In the case of alternating voltage used in everyday life, the phase (supply) and neutral wires are used for this. Where the electric current comes from is clear; but where does the electricity go? To the ground! A little simplified, but by and large it is true. Right into the ground.
The substation transformer has a ground connected to a separate line wire. This is the same “zero” in our sockets. Those who are especially curious can verify this by examining a regular transformer substation with overhead lines. 3 wires came in, 4 came out. At the input there are three phases of high voltage, at the output there are three phases of low voltage and a neutral wire.
Now let's move on to the main thing - human protection.
Grounding in an apartment
The most reliable way to protect against electric shock at home is to ground electrical appliances. After all, many of our home assistants have metal (read: conductive) cases, and as a result of a break or damage to the insulation, the phase wire may touch the body of the device. And then touching him becomes deadly...
To avoid trouble, the body of the device is connected to the ground. Now, when a phase hits the housing, a short circuit occurs and the protection is triggered, cutting off the current supply.
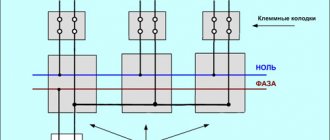
In modern apartments, electrical wiring is carried out according to a three-wire circuit:
•
phase;
•
zero;
•
Earth.
Grounding of electrical appliances occurs through the third contact of the plug and socket. The situation is more complicated in houses where the wiring is installed in a two-wire circuit and there is no ground wire in the sockets. In this case, the grounding wire will have to be drawn directly from the device body.
Where can I get “land” in an apartment in a multi-story building? The answer is simple: in the electrical panel installed on each floor.
Before performing a grounding installation (it is better, of course, to do this with the participation or supervision of a professional electrician), carefully examine the electrical panel. After all, if there is no reliable grounding at the switchboard, connecting the apartment’s grounding wire to it is not only in vain, but also dangerous!
Let's explain with an example. The neighbor has a short circuit. The current will travel the following path: the neighbor’s phase – the neighbor’s “zero” – the floor electrical panel – your ground wire – the body of your device!
Will there be step voltage?
Step voltage appears when a live wire touches the ground and current flows across the surface of the earth.
Theoretically, if all the requirements for the grounding loop specified in PUE-7 clause 1.8.39 are met, when using grounding instead of zero, step voltage should not arise, but in practice these rules are not always followed, especially if the loop was made independently and its primary and no repeated checks were carried out.
| Advice! For greater safety, it is recommended to place the ground loop not under pedestrian areas, but under flower beds and other green areas. |
Will electrical appliances work?
The only thing for which the order of connecting zero and phase does not matter is the operation of electrical appliances. For these devices, only the voltage value in the outlet is important, and it does not change depending on which wire is connected where.
From the point of view of electrical engineering, it does not matter which wire connects the neutral terminal of the socket to the neutral of the transformer - N if the connection is correct or PE if it is incorrect.
| Information! In the TN-CS power supply system, the individual wires N and PE are separated not in the substation, but in the input panel to the building, after which they are connected to the transformer with a common wire PEN. |
Using a multimeter
A more complex method is to find the grounding conductor using a multimeter. It is based on the fact that an equalizing current flows through the neutral wire and therefore there is a small potential relative to ground at the zero terminal.
To find the neutral wire with a multimeter, you must have access to an electrical panel or a properly connected outlet:
- 1. Using an indicator screwdriver in the electrical panel, the phase terminal is determined;
- 2. The voltage between the phase-zero and phase-ground terminals is measured with a multimeter, the resulting values are recorded;
- 3. operations are repeated in the transition or installation box;
- 4. The obtained values are compared with the recorded ones.
This method of distinguishing zero from ground can be used in the new five-wire TN-S power supply system. In older four-wire TN-CS grounding schemes, the building is connected to the neutral of the transformer by a PEN wire, which is divided into PE and N by the input panel in the house, so the multimeter readings will be the same in both cases.
Will the electric meter run?
Some who want to “save”, or rather steal electricity, are interested in what will happen if they connect the ground instead of zero ? Maybe the counter will stop or even rotate in the opposite direction? These lovers of “freebies” can sleep peacefully - the electricity meter readings will not change.
To operate, the meter measures two parameters:
- Mains voltage. It is determined by the phase and neutral wires coming from the access electrical panel or power line pole.
- Current flowing through a phase wire. It does not depend on whether electrical appliances are connected to neutral or ground.
It should be noted that modern metering devices work perfectly and count electricity consumption even if ground is connected to the terminals instead of zero.
To “save” it is necessary to change the connection of the incoming cable at the connection to the electric meter, which is located in a sealed box, which is fraught with a large fine when the meter is checked by an electric company inspector.
Ground pin in socket
If you have access to the inside of the panel, a known-to-be-correctly connected outlet, or grounded structures (including water pipes), you can use the resistance measurement method:
- 1. Turn off the circuit breaker that breaks both wires - phase and neutral. If the line is disconnected by a single-pole circuit breaker, then it is necessary to turn off the upstream disconnector.
- 2. Using an ohmmeter, sequentially measure the resistance between the grounded elements and the cable being tested. It will be insignificant when connected to a grounding conductor and at least 1 mOhm when connected to a neutral or phase wire.
| Important! The measurement results will be correct only if the insulation of all electrical appliances connected to the network is properly insulated. |
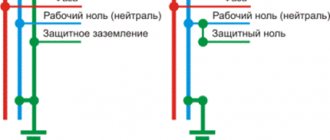
Connection of zero and ground
To organize protective grounding, it is necessary that three wires be connected to a private house, and five to an apartment building. This power supply system is called TN-S and is laid in new neighborhoods and when replacing existing power lines. But what should people living in old houses do? What happens if you connect zero and ground directly in the socket?
According to the Electrical Installation Rules, such a connection is permissible, but not in an outlet, but in an input panel in an apartment building or on a power line pole near a private house.
The PUE Chapter 1.7 specifies the requirements for the TN-CS power supply system. This power supply scheme is carried out through four wires - three phases L1, L2, L3 and a combined PEN, which performs the functions of neutral and grounding simultaneously.
To increase the safety of people living in the house, the connection point must be connected to the building's ground loop. Otherwise, instead of protective grounding, you will get a protective grounding and, if the wire between the building and the supply transformer breaks, the grounded housings of electrical appliances will be energized.
I also recommend reading an article about the operation of an RCD when the neutral wire breaks:
This regulatory document indicates whether the grounding can be connected to zero. According to the PUE clause 1.7.135, after separation, and even more so in a five-wire TN-S power supply circuit, connecting these wires is not allowed.
In addition, the grounding conductor must be connected to the equipment directly, without circuit breakers or disconnectors.