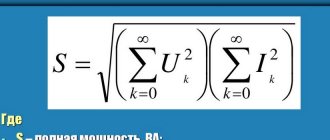
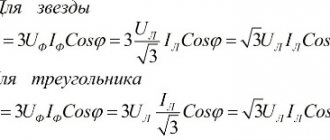Watt concept
Watt (W) is a unit of electrical power - energy consumption over a certain time. 1 watt is equal to the same number of joules (J) of electricity for 1 second.
The name of this unit of measurement comes from the name of the British scientist James Watt, who first proposed using horsepower as a universal calculation for the technical performance of machines.
Designation and history
Before proceeding to a detailed consideration of the watt, it is necessary to give it the correct designation. Watt is a unit that is used to measure power. Most often the name is written in abbreviated form - Tue. The English abbreviation for quantity is W.
The history of the unit of measurement W begins at the end of the century before last. It was first used in the UK. But this does not mean that the need to measure power arose at that time. It was defined before the appearance of this unit.
To measure a physical quantity that many today associate primarily with electricity, already in the 18th century a unit called horsepower was used. It was based on the power of riding horses. The tradition of measuring in horsepower continues today, having been successfully transferred from horses to cars. Today, one horsepower is equal to approximately 735 watts.
Before the introduction of the watt, horsepower varied from country to country. The unit W gets its name from the scientist who is considered the progenitor of the Industrial Revolution. His name was James Watt. He lived in the 18th-19th centuries and became famous for creating a universal steam engine.
The scientist devoted much of his work to the study of power. It was he who first began to use horsepower to measure it. 63 years after his death, the same unit that is still in use today was introduced and named after him.
Converting watt to kilowatt
By analogy with other units of measurement, the prefix “kilo” means 1000, so the formula for converting watts to kilowatts is as follows:
1 kW = 1000 W
If the indicated parameters of the iron are 1.8 kW, then in the corresponding translation this figure is 1800 W.
When converting back, the number of watts is divided by 1000: with an incandescent lamp power of 100 W, this criterion equals 0.1 kW.
The value of this equipment characteristic is easy to find out by studying the technical documentation of the product or the markings applied by the manufacturer on the case.
Total electrical power value
Sometimes it is necessary to calculate the total power of household consumers installed in the house. This is necessary for:
- correct choice of cable cross-section when installing electrical wiring;
- selection of control devices, including circuit breakers, electric meters, etc.;
- layout of the wiring system in the house.
Ultimately, correct accounting of the total energy intensity of household appliances ensures the operational reliability of electrical wiring and the safe operation of household electrical appliances.
To calculate the highest possible power of household electrical appliances, you should add up the number of watts indicated in the technical documentation of the equipment or directly on the equipment itself. When performing the calculation, all values must be converted accordingly to the same unit of measurement, taking into account the procedure described above.
What is the difference between a kilowatt and a kilowatt hour?
Many consumers habitually refer to electricity consumption indicators recorded by an electric meter as kilowatts. But in fact, this indicator is measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh), which is not the same thing at all.
Energy consumption in kWh is determined by the amount of power expended during a certain time.
An example of such a calculation:
- an incandescent lamp of 0.06 kW is used for lighting;
- for 6 hours of operation (approximate operating time during the day), this device will consume electricity 0.06 × 6 = 0.36 kWh;
- per month, the consumption for the specified lamp will be 0.36 × 30 = 10.8 kW*h.
The difference between kilowatt and kilowatt hour
In electrical engineering, a quantity called a kilowatt-hour is determined by electric meters. Due to the similarity of names, kilowatt-hours are sometimes confused with kilowatts. In fact, these are different parameters.
KWh is used to determine the amount of electrical energy produced or consumed per unit of time. For example, a receiver with a flow rate of 1 kWh determines the amount of energy consumed by a 1 kW device over 1 hour.
Unlike a kilowatt-hour, a kilowatt is a unit of power that characterizes the intensity of electricity consumption.
How kW and kW∙h are related can be seen using the example of a TV (200 W). The estimated viewing time of the television program was 1 hour. This could mean that the TV used 200 watts during this period. Multiplying 200 W by 1 hour, we get 200 W * 1 hour = 200 Wh = 0.2 kWh.
We advise you to study Contactors and magnetic starters
At the beginning of the electrification era, electricity was used only for indoor lighting. Those using this service understood that a 100 W light bulb would generate exactly 1 kW in 10 hours. With the beginning of the use of kW⋅h when calculating energy consumption, people began to better understand what they had to pay for. He now has the opportunity to regulate spending by properly selecting lighting equipment.
Watt concept
Watt (W) is a unit of electrical power - energy consumption over a certain time. 1 watt is equal to the same number of joules (J) of electricity for 1 second.
The name of this unit of measurement comes from the name of the British scientist James Watt, who first proposed using horsepower as a universal calculation for the technical performance of machines.
Converting watt to kilowatt
By analogy with other units of measurement, the prefix “kilo” means 1000, so the formula for converting watts to kilowatts is as follows:
1 kW = 1000 W
If the indicated parameters of the iron are 1.8 kW, then in the corresponding translation this figure is 1800 W.
When converting back, the number of watts is divided by 1000: with an incandescent lamp power of 100 W, this criterion equals 0.1 kW.
The value of this equipment characteristic is easy to find out by studying the technical documentation of the product or the markings applied by the manufacturer on the case.
Total electrical power value
Sometimes it is necessary to calculate the total power of household consumers installed in the house. This is necessary for:
- correct choice of cable cross-section when installing electrical wiring;
- selection of control devices, including circuit breakers, electric meters, etc.;
- layout of the wiring system in the house.
Ultimately, correct accounting of the total energy intensity of household appliances ensures the operational reliability of electrical wiring and the safe operation of household electrical appliances.
To calculate the highest possible power of household electrical appliances, you should add up the number of watts indicated in the technical documentation of the equipment or directly on the equipment itself. When performing the calculation, all values must be converted accordingly to the same unit of measurement, taking into account the procedure described above.
Designation kW
Kilowatt is written as kW. It is a unit of power divided by the derived SI unit watt. Watt denotes the power at which 1 joule (J) of work is performed or energy is consumed in 1 second.
Another watt is defined as the speed of work at which a constant motion of a body of 1 meter per second is ensured, if at this time a force equal to 1 newton is overcome, going in the direction opposite to the direction of movement of the object.
The power of household appliances is measured in kilowatts. The abbreviation kilowatt denotes work:
- lamp;
- TV;
- vacuum cleaner;
- microwave;
- refrigerator;
- combine;
- mixer.
Relationship between quantities
To better understand the purpose of this unit, you should have an idea of what power is. Many people think it's just power. However, in physics these are completely different quantities that have almost nothing to do with each other. To put it as briefly as possible, ignoring some minor nuances, power is the rate at which an object consumes energy.
You may be interested in what is called phase and zero in a home electrical network
For example, a light bulb in a lighting fixture may glow brightly or dimly. It all depends on the speed at which it consumes electrical energy. If it burns brightly, it means energy is being consumed quickly. When the light coming from a lamp is dim, it consumes energy at a low rate. Even simpler, you can say this:
- if the lamp glows brightly, it means its power is high;
- if its light is dim, it means it has little power.
The same applies to any other devices powered by electricity. But when they talk about power, they don’t always mean electrical appliances or some other objects related to electricity.
For example, if you take a moving car, it has a certain force. The faster the energy generated by the fuel in the gas tank is consumed, the more powerful the car. True, motorists measure the power of their “iron horses” in other units called horsepower. However, this does not mean that traditional watts are not applicable for this case. One unit can easily be converted to another, knowing that one horsepower is approximately 735 watts. There are three types of power:
- Electric. This is what they mean when they talk about light bulbs or other electrical appliances.
- Mechanical. The “horsepower” of a car falls into this category.
- Thermal. How much thermal power a particular object has can be judged by its temperature.
Power is the rate at which energy is consumed. Trying to understand what 1 watt is equal to, what energy and for how long an object must be used so that it can be said that its power is equal to one watt, physicists derived such a quantity as power based on other simple quantities - time and energy. They took their basic units of measurement and agreed that if a physical body receives or produces 1 joule of energy in 1 second, then it has a power of 1 watt.
You may be interested in Letter designations of elements on electrical diagrams
This simple definition is based on the formula: N=A/t. The designation of the signs here is as follows:
- N is the designation for power;
- A in physics traditionally denotes work, which is measured in the same units as energy;
- t is a symbol for time.
If it is necessary to determine the mechanical value, then another formula based on other values can be used for this purpose: N=FV. Simply put, you need to multiply force by speed.
Converting kW to W and vice versa
Similar to other units of measurement, the prefix “kilo” means 1000. To convert a watt to a kilowatt, you need to use the formula:
If the mixer says 1.6 kW, this means that its power in watts will be 1600. If you convert it back, then the number of watts is divided by 1000. An incandescent lamp has a power of 100 W, which is the same as 0.1 kW.
Example of conversion of 2 kilowatts (2 kW): 2*1000=2000 W.
It is easy to find out the power of the device - you will need to study the technical documentation for the device or look at the markings located on the case.
Now you can easily calculate and convert units. There are various online calculators for this. They enter a query into the search bar and go to the site.
Submultiples and multiples
If the power is too large or, conversely, small, then using the usual watt as a unit of measurement will be inconvenient. In this case, multiples and submultiples will come to the rescue. If we talk about only one light bulb and for short periods of time, then the power will not be very large. For example, in an hour such a lighting device can generate about 100 joules of energy.
But when you need to determine the power of not one, but several such light bulbs (tens, hundreds, thousands), and not in one hour, but, for example, in a month or a year, then the number will turn out to be cumbersome. It is advisable to use not watts, but their multiple designations - kilowatts (kW), megawatts (MW), gigawatts (GW).
You might be interested in: The unit of measurement is kilowatt and what is measured in kW
The meaning of multiples is easily determined by the prefixes, which are used in the same way as with most other units. The prefix “kilo” indicates 1000 units, “mega” indicates a million, and “giga” indicates a billion.
Most often in practice kilowatts are used. In one such multiple unit there are a thousand watts. The same applies to submultiples, which are used in cases where it is necessary to indicate low power, which is tens, hundreds, thousands and millions of times less than 1 W. For example:
- a tenth of a vata is a decivat;
- hundredth part - centiwatt;
- thousandth - milliwatt.
Some medical devices use microwatts as a unit of measurement. Each such unit is a million times smaller than a watt.
Difference between kW and kWh
Many users refer to electricity consumption readings as kilowatts, but this is incorrect.
Important! Electricity consumption in kWh is calculated as the amount of power spent over a certain time interval.
It is worth considering an example:
For lighting, an incandescent lamp with a power of 0.07 kW is used. For 6 hours of electricity operation (this is the approximate time during which the lights are on per day), the device consumes energy 0.07 * 6 = 0.42 kWh.
For a month, the cost of an incandescent lamp will be 0.42 * 30 = 12.6 kWh.
Using the same method, the total consumption of electricity for a month is calculated, knowing the duration of the device or appliance being turned on and its power. Subsequently, it is possible to establish the amount of savings achieved due to the operation of less energy-consuming equipment and a more careful attitude to resource consumption.
In the SI system of units there is no such quantity as kilowatt-hour. This is an off-system derivative, which was invented solely to record the electrical energy used or produced.
Important! In Russia, the concept of “kilowatt-hour” is used as a unit of measurement based on GOST 8.417-2002. It indicates the exact name, decoding and scope of application.
When choosing equipment in a store, you should pay attention to the body. The front panel always shows the letter W and numbers next to it. This is the power of the device, measured in Watts. In other words, the rate at which electricity is consumed. A kilowatt is 1 W multiplied by 1000. The kilowatt-hour indicator is used to measure energy in everyday life. This is the electricity that the device produces or consumes in 1 hour.
Power measurement in kW
The most well-known way to measure power in everyday life is to look at the meter. On it you can see not only electricity consumption.
A modern meter shows light consumption at night, during the day, on holidays, as well as power P
Not all meters show power, but all models measure:
- number of disk revolutions in one kW per hour;
- number of pulses, how many times the 1 kWh indicator lights up.
If the information is available, the user can easily determine the value.
Using a current clamp meter, you can compare the actual reading with what the meter shows
There is a special meter for the socket. Its other name is energy meter or wattmeter. The device is sold in electrical stores. The device will help measure the following indicators:
- currently consumed power;
- consumption over a certain period of time;
- current;
- voltage;
- costs at specific tariffs.
You might be interested in: Connecting a chandelier
The wattmeter is inserted into a socket on the wall, the device is placed into the socket of the device, and all the information appears on the screen