What is a viscous all-wheel drive coupling, how it works and what it is needed for
An important element in a car is the all-wheel drive viscous coupling, which is also called a viscous coupling. This element is included in the design of the car transmission. The viscous coupling is responsible for the functioning of the transmission mechanism and ensures equalization of wheel torque. The mechanism is important and necessary; a lot depends on its proper operation.
What is a viscous coupling
Let's begin to understand what an all-wheel drive viscous coupling is. This information will be useful to many motorists who always want to know a little more about the structure and design of their “iron horse”. The viscous coupling is not a new invention, as it was invented in 1917. True, it found its application only in 1964. Then this mechanism appeared in the English car Interceptor FF. Since then, the viscous coupling has been used as a lock for the center self-locking differential on vehicles with four-wheel drive.
Appearance of the Haldex all-wheel drive clutch
The main difference between a viscous coupling and a fluid coupling and a transformer is the transmission of torque through the special properties of the fluid located inside the mechanism.
How viscous couplings for transmissions are designed and work
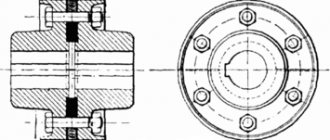
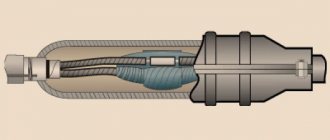
First, let's study the design of the all-wheel drive viscous coupling. This mechanism has the shape of a cylinder, the design of which is sealed. The main components of the design are flat-shaped perforated disks and a special liquid. Disks are divided into two groups, which differ in connection with the shafts. One group of disks is connected to the master, the other to the slave. During operation, the viscous coupling disks alternate with each other, but are at a minimum distance from each other.
Viscous coupling in section
About 80% of the internal structure is dedicated to a special silicone fluid. It acts as a connecting element between the disks. This liquid is characterized by high kinematic viscosity. At the same time, it does not have lubricating properties. Such features allow the fluid to ensure maximum closure of the disks in the presence of a difference in angular velocity. This is the basic principle of operation of a viscous coupling.
Scientists have created a unique organosilicon liquid that becomes less viscous when heated. In this case, the siloxane becomes so thick that it even shows signs of a solid substance. This allows the viscous coupling to transmit torque under conditions of different rotation speeds of the parts.
The viscous coupling has found wide application in automatic systems operating on the all-wheel drive principle. If driving conditions are within normal limits, the force from the motor is transmitted to one axle. A second axle operating in freewheel mode is connected through the coupling. When the main axle slips, the viscous coupling is blocked, which causes the force from the motor to be distributed to the driven axle.
When the car drives out onto a flat road, the fluid returns to its previous state, the blocking is removed from the viscous coupling and the second axle again operates in freewheel mode. This is roughly how a viscous all-wheel drive coupling works.
Pros and cons of viscous coupling
Viscous couplings cannot be called an ideal mechanism, since along with the advantages there are also disadvantages. First, let's study the positive features of the mechanism:
- simple, even primitive, design;
- the strength of the case is so high that it can easily withstand a pressure of 20 atmospheres;
- the low cost of a new part makes its replacement affordable for every motorist;
- minimal maintenance;
- low percentage of breakdowns.
Removed viscous differential clutch
Let's dilute this picture with negative characteristics:
- maintainability is not typical for such a mechanism, therefore, in the event of a breakdown, it is replaced with a new one;
- long-term operation in difficult conditions increases the likelihood of overheating of the mechanism;
- no manual locking;
- incomplete automatic blocking;
- delay in response;
- inability to connect the all-wheel drive viscous coupling to the ABS system;
- all-wheel drive is uncontrolled;
- reduction of vehicle clearance when installing large couplings.
Be that as it may, all-wheel drive viscous couplings are actively used and so far no one has been able to present a worthy alternative to the world community.
What kind of oil to pour into the all-wheel drive clutch
The all-wheel drive viscous coupling, like other mechanisms, uses a lubricant in its operation, which is a special oil. All manufacturers claim that there is no need to change it throughout the entire period of operation of the vehicle. This statement does not always correspond to the actual state of affairs.
Fill the four-wheel drive clutch with oil
The need for an oil change may be indicated by small kicks in the rear of the car when pressing the gas pedal or making a turn. This behavior of the machine may indicate a damaged condition of the viscous coupling oil.
It is better to carry out the replacement at a service station, since this work is not the easiest. To replace it, you must choose the oil that is indicated in the instructions for the car. It often turns out that the specified lubricant cannot be found on sale - many motorists face this problem. We have to look for a replacement. A worthy option is Ravenol TF0870 lubricant.
Classification of electric couplings
In many cases, electrofusion couplings are classified according to the application in which they are used. An electromagnetic friction clutch is very often used. It has the following qualities:
- The device can be used to reduce the permissibility of the influence of impulse loads.
- At idle, the design features create small losses. This moment determines that important elements do not heat up during operation.
- It is possible to quickly start the mechanism even if, for example, it is under high load.
The type of mechanism under consideration is divided into several key types:
Quite often there is an electromagnetic brake clutch, which can reduce the number of revolutions during operation.
An embodiment of the air conditioning blower is provided in the form of a unit, which consists of the following elements:
- Electromagnetic type coils. It is made using specialized alloys, which differ in some features. The coil is required to directly generate the electromagnetic field.
- Pressure type plates. Such a structural element should be characterized by greater strength.
- A pulley that transmits force from an electric motor. A drive of a similar type has become very widespread, as it guarantees protection of the device from overheating under excessive load. By changing the pulleys, it is possible to regulate the number of revolutions at the output.
In this case, electricity is supplied to the coil, which creates an electromagnetic field. Due to this, the pressure plate is attracted to the pulley. This movement gives freedom to the shaft, and the mechanism begins to work.
Compressor units have become very widespread. That is why it is necessary to pay attention to the following defects:
- Very often you can encounter a situation where a pulley bearing is deformed. In this case, it is enough to replace the element.
- The pressure plate is made of thin metal, so during use it can change its shape. In addition to this, the problem appears if the gap is set incorrectly.
- There is a situation where the clutch itself burns out. It is very often associated with a high voltage that is applied to the coil.
The development of new technologies has determined that an electromagnetic clutch is installed in cars. It is divided into several different types depending on the drive:
- Hydraulic. This embodiment differs in that the force is transmitted due to the fluid in the system. Oil and water are perfect for transferring force. However, the hydraulic drive is currently characterized by relatively low reliability.
- Mechanical. This device is distinguished by the fact that force is transmitted by combining a variety of components. An example is sprockets, gears and other parts.
- Electromagnetic clutch.
Choosing the right lawn mower
The latter type of mechanism is very popular. It is also classified into several key types:
- According to the friction criterion, wet and dry are distinguished. These days, implementation options have become extremely popular, which, as a rule, will work exclusively with the addition of oil.
- The classification is also based on the mode of inclusion: intermittent and frequent.
- There are couplings with one or more driven discs. The choice depends on what operating characteristics are needed.
- Based on the type of control, there are also several main types of mechanism. An example is mechanical, hydraulic and combined.
Another group includes electromagnetic powder couplings. They are provided by a combination of substances that, when acting mutually, are capable of providing a strong bond.
This modern embodiment occurs when it is necessary to ensure the displacement of the connected components relative to each other at the time of operation.
The operating principle of SUV all-wheel drive clutches
A number of all-wheel drive systems have a special clutch, with which the level of torque transmission to the vehicle axle is regulated.
By the way, clutch failure is becoming one of the common causes of all-wheel drive failure. The coupling may fail if its maintenance is not carried out in a timely manner:
- do not change the oil in the coupling;
- Ignore the ringing of the bearing.
Volkswagen has achieved the greatest success in the development of all-wheel drive clutches. She developed the 4Motion system, which should be discussed in more detail.
4Motion system and Haldex coupling
The technology began to be used two years before the Millennium.
Before this, the all-wheel drive of German cars was based on viscous couplings. The use of the Haldex clutch was a revolution in the field of all-wheel drive. This coupling:
- friction;
- has a large number of disks;
- controlled electrohydraulically.
Its use made it possible to create cars with automatically connected all-wheel drive. By the way, the Haldex coupling is now installed not only on German cars, but also on cars from other European manufacturers.
4th generation coupling
Modern all-wheel drive vehicles are equipped with a 4th generation clutch. The principle of its operation is similar to the principle of operation of couplings of previous generations. However, the device already has an electronic pump. The speed difference is now of secondary importance; the clutch operates based on the exchange of signals between various sensors and the control unit.
Thus, it can be noted that a modern all-wheel drive clutch is a fairly effective device that makes it possible to efficiently distribute torque between axles automatically, without human intervention.
A significant disadvantage of such couplings is that they can fail under heavy loads. And replacing or repairing them is expensive.
Ventkam.ru
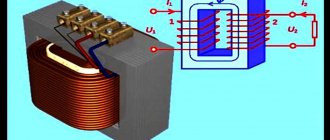
An electromagnetic clutch is a device that connects the ends of two shafts to transmit rotation. An electromagnetic asynchronous clutch is designed on the principle of an asynchronous motor and serves to connect two parts of the shaft. A pole system is placed on the driving part of the shaft, which is a system of salient poles with excitation coils.
The principle of operation of the coupling is similar to that of an asynchronous motor, only the rotating magnetic flux here is created by the mechanical rotation of the pole system. Torque from the driving part of the shaft to the driven part is transmitted electromagnetically. The coupling is disconnected by turning off the excitation current.
A typical electromagnetic clutch consists of two rotors. One of them is an iron disk with a thin annular protrusion at the periphery. On the inner surface of the protrusion there are radially oriented pole pieces equipped with windings through which excitation current from an external source is passed through slip rings on the shaft. The other rotor is a cylindrical iron shaft with grooves parallel to the axis. Insulated copper bars are inserted into the grooves, connected at the ends by a ring copper collector. This rotor is free to rotate inside the first and is completely enclosed by its pole pieces.
READ ALSO: Building a summer shower at the dacha
When the excitation current is turned on and one of the rotors, say the second (which is typical for ship practice), is rotated by the engine, the magnetic field lines created by the excitation current are crossed by the conductors of this rotor (copper bars) and an electromotive force is induced in them. Since the copper bars form a closed circuit, a current created by the induced EMF flows through them, and this current generates its own magnetic field. The interaction of the rotor fields is such that the driven rotor is carried along with the leading one, albeit with a slight delay. The described principle of operation of the electromagnetic clutch is the same as that of an asynchronous electric motor with a squirrel-cage rotor.
Electric current control allows for remote control of the clutch (smoothly engaging and disengaging it). Therefore, it is used in automation and telemechanics. The electromagnetic clutch has a very wide range of applications. So, this part is used in diesel locomotives, metal-cutting machines and similar mechanisms. However, at the same time, the couplings used in all these devices and mechanisms are far from the same. So, even the electromagnetic clutch of a gazelle differs from the electromagnetic clutch of a Kamaz.
How to change a four-wheel drive clutch bearing
One of the characteristic diseases of couplings is bearing noise. Moreover, this is relevant both for old viscous couplings and for modern electrically controlled ones. If the bearing starts to ring, it needs to be replaced to avoid more serious consequences. This can also be done at home. The main thing is to have certain theoretical knowledge and direct hands. Of course, the repair technology is somewhat different, depending on the make and model of the car. But the general principle is this:
- It is necessary to drive the car into a pit or hang it on a lift.
- Identify the cardan and gearbox under the bottom of the car. The clutch itself is attached to the gearbox. Often a number of operations are also carried out to disconnect the elements of the all-wheel drive system from each other. Such manipulations make it easier to remove the coupling. At the same time, you can carry out preventive maintenance on other elements of the system.
- Just in case, drain the oil from the gearbox.
- Dismantle the coupling and remove the bearing.
- Remove in all accessible places all rust that has formed during operation of the old bearing.
- Install the new bearing in the place where it is supposed to be, oriented correctly.
- Carefully assemble everything in the correct order and seal it.
The instructions, it is worth repeating, turned out to be quite general and short. But each specific case has its own characteristics and difficulties. For someone, for example, a new bearing does not fit into place, then you can use a sledgehammer or hammer in the repair, with a great deal of accuracy.
How does the device work?
The principle of operation of the device resembles the operation of an asynchronous motor, but unlike it, the magnetic flux in this case is created by rotating the pole system. The transmission of rotation from one part of the shaft to another is transmitted electromagnetically. When the power supply is turned off, the device is disconnected.
The design of the part is based on two rotors, each of which is an iron disk with a thin annular protrusion on the periphery. Pole pieces with a winding through which current is transmitted are located on the inner surface of the protrusion. The second rotor is presented in the form of a cylindrical iron shaft, equipped with special grooves, which rotates around the first rotor.
By controlling the electric current, you can control the clutch from a distance, namely, connect and disconnect it, which is especially important in automation. They do not require any mechanical connections, which ensures fast operation and no downtime.
What kind of oil to pour into the all-wheel drive clutch
Depending on the make and model of the car, the oil in the all-wheel drive clutch must be changed after 30 and 60 thousand kilometers; some sources indicate a figure of 100,000 kilometers. But it’s better not to delay. The oil change process itself does not pose any serious difficulties. The coupling has a drain hole and a filler neck. The oil change process is quite typical:
It is worth emphasizing that the most common Haldex couplings are located in the final drive.
There have been cases when, during car maintenance, servicemen confused the filler and drain holes of the coupling itself and the gearbox, which led not to fatal, but to unpleasant consequences.
Of course, those who are serviced by official car repair shops should not rack their brains over finding the necessary oil for the clutch.
As for the rest, those who love and want to service the car with their own hands, the following options are recommended:
- go to an official car service center and find out what kind of oil local specialists use;
- go to a forum dedicated to a specific make and model of car, and there;
- contact the developers of a particular coupling and check with them for information.
Types of ETM couplings
Conventionally, ETM couplings can be divided into three groups:
- Serrated. Rotation in this case is transmitted using two gear-type rings, the connection and disconnection of which occurs using the magnetic field generated by the coil. Such devices can be used in any conditions.
- Multi-disc. Torque in such devices is transmitted through a package of disks. For proper operation of such couplings, they must be lubricated regularly.
- Single-disc. Designed for use in dry environments.
In turn, gear couplings are divided into:
- DC devices;
- with slip rings;
- disconnecting coils with a fixed body;
- disconnecting with a slip ring and a spring;
Multi-disk devices have the following classification:
- with slip ring;
- with a fixed body.
There are also other classifications. All devices are divided into several types depending on the following parameters:
- rotation principle;
- rotor design;
- power supply method;
- cooling method;
- execution type.
In order for the electromagnetic coupling to effectively cope with the tasks assigned to it, it should be positioned horizontally in a place protected from water and emulsion. The environment must not be explosive. It should not contain concentrated gases, aggressive vapors, liquids or conductive dust. A high-quality device must remain resistant to frost and high relative humidity. Its transportation must be carried out in a special container.
All-wheel drive diagram with electromagnetic clutch
On many cars, all-wheel drive is plug-in. All-wheel drive on Chery Tiggo cars is arranged in the same way; the rear-wheel drive here is connected automatically, through an electromagnetic clutch.
The clutch is controlled by the four-wheel drive control unit. The operating principle of an electromechanical clutch is almost the same as that of a clutch. When voltage is applied to the clutch, the discs inside the clutch are pressed against each other and torque begins to be transmitted through them to the rear wheels.
All-wheel drive is engaged on the Cherry Tiggo only when the front wheels slip, and approximately after the second rotation of the wheel. When all-wheel drive is no longer needed, it turns off. The drive also turns off when a certain speed threshold is exceeded, because the clutch is not designed for high speeds.
There is a four-wheel drive check lamp on the Cherry instrument panel. When the ignition is turned on, the lamp lights up and the system performs a self-test. If everything is in order, the lamp goes out. If there is a fault, the lamp will continue to light.
Unfortunately, there are no identifying marks in the car that the drive has turned on. But you can easily understand this when you get stuck and start slipping. When the rear wheel drive is engaged, you will feel a slight push, and the car will slowly begin to climb out of the rubble.
Torque is transmitted to the rear wheels through the transfer case (2), front driveshaft (4), electromagnetic clutch (5), rear driveshaft (6), rear axle gearbox (7) and rear wheel drives.
All-wheel drive transmission diagram
1 — gearbox, 2 — transfer case, 3 — front wheel drives, 4 — front cardan drive, 5 — electromagnetic clutch, 6 — rear cardan drive, 7 — rear axle gearbox, 8 — rear wheel drives.
The transfer case is rigidly mounted on the gearbox housing. The drive for the transfer case is a differential box. The transfer case itself is two-stage. There is no center differential in the transfer case, and the redistribution of torque between the axles is performed by an electromagnetic clutch depending on road conditions.
The driveshafts are made of thin-walled steel. The electromagnetic clutch transmits torque to the rear wheels only when the clutch is partially or completely blocked from the signal from the all-wheel drive control unit.
The all-wheel drive control unit is located under the driver's seat. The drive unit receives information from the engine control unit and, based on the received data, turns the clutch on or off, thus supplying or removing torque to the rear wheels.
The block receives the following information:
— engine load (from the engine ECU)
— longitudinal acceleration of the vehicle (from the acceleration sensor under the instrument panel console)
— vehicle speed and wheel speed difference (from wheel sensors)
— braking mode (from the ABS unit)
The electromagnetic clutch requires no maintenance.
Operating principle of electromagnetic clutch
An electromagnetic clutch is a device that connects the ends of two shafts to transmit rotation. An electromagnetic asynchronous clutch is designed on the principle of an asynchronous motor and serves to connect two parts of the shaft. A pole system is placed on the driving part of the shaft, which is a system of salient poles with excitation coils.
The principle of operation of the coupling is similar to that of an asynchronous motor, only the rotating magnetic flux here is created by the mechanical rotation of the pole system. Torque from the driving part of the shaft to the driven part is transmitted electromagnetically. The coupling is disconnected by turning off the excitation current.
A typical electromagnetic clutch consists of two rotors. One of them is an iron disk with a thin annular protrusion at the periphery. On the inner surface of the protrusion there are radially oriented pole pieces equipped with windings through which excitation current from an external source is passed through slip rings on the shaft. The other rotor is a cylindrical iron shaft with grooves parallel to the axis. Insulated copper bars are inserted into the grooves, connected at the ends by a ring copper collector. This rotor is free to rotate inside the first and is completely enclosed by its pole pieces.
READ ALSO: Features of modern wooden windows
When the excitation current is turned on and one of the rotors, say the second (which is typical for ship practice), is rotated by the engine, the magnetic field lines created by the excitation current are crossed by the conductors of this rotor (copper bars) and an electromotive force is induced in them. Since the copper bars form a closed circuit, a current created by the induced EMF flows through them, and this current generates its own magnetic field. The interaction of the rotor fields is such that the driven rotor is carried along with the leading one, albeit with a slight delay. The described principle of operation of the electromagnetic clutch is the same as that of an asynchronous electric motor with a squirrel-cage rotor.
Electric current control allows for remote control of the clutch (smoothly engaging and disengaging it). Therefore, it is used in automation and telemechanics. The electromagnetic clutch has a very wide range of applications. So, this part is used in diesel locomotives, metal-cutting machines and similar mechanisms. However, at the same time, the couplings used in all these devices and mechanisms are far from the same. So, even the electromagnetic clutch of a gazelle differs from the electromagnetic clutch of a Kamaz.
All-wheel drive of Renault and Nissan crossovers: expert analysis “Behind the Wheel”
“Behind the Wheel” tells how the all-wheel drive transmission works on the large family of crossovers from the Renault-Nissan alliance and whether it can actually overheat when driving off-road.
Renault > Captur
Renault > Duster
Renault > Koleos
Nissan > X-Trail
Nissan > Terrano
Nissan > Qashqai
To understand the features of all-wheel drive crossovers, you need to start, oddly enough, with their single-wheel drive counterparts.
So, a modern front-wheel drive crossover is an ordinary car with a hatchback or station wagon body with wheels slightly larger in diameter and a slightly increased ground clearance (by only 25 - 75 mm). In addition, it is most often created on the platform of a popular passenger car. On all crossovers created in this way, the engine is located transversely, and the driving wheels, of course, will be the front ones.
However, not all companies agree with the presence of only such “under-drive” crossovers in the range of cars produced.
All-wheel drive of a modern crossover
Practice shows that the recipe for creating an all-wheel drive crossover is approximately the same for all non-premium companies. The engine is mounted transversely on the right side of the engine compartment. The gearbox (it doesn’t matter whether it’s manual, variator or automatic), naturally, also turns out to be installed transversely - only in front of the driver. All the shafts inside it are also located transverse to the longitudinal axis of the car. And the drive shaft, which transmits torque to the rear axle, runs along this axis, through the entire car. Therefore, it is necessary to use a bevel gear at the front and a driveshaft going to the rear axle.
The driveshaft is connected to a clutch that controls the transmission of torque to the rear axle. Further, since the rotation must be transmitted at an angle of 90 degrees, the use of a second angular gearbox combined with the differential is inevitable. From the differential, the drives transmit rotation to the rear wheels. This scheme is used on cars from Nissan (Terrano, Qashqai, X-Trail) and Renault (Duster, Kaptur and Koleos).
After the primary and secondary shafts of the gearbox, a main gear is installed, which reduces the rotation speed to that required to rotate the wheels. Let us remind you that the connection with the front wheel drives is not direct, but through a differential.
The transmission, be it automatic, CVT or manual, is somewhat different from the usual one installed on front-wheel drive cars. On the left, the gearbox includes a splined and cylindrical part of the housing of the internal joint of the left wheel drive. Everything here is like any front-wheel drive car. But on the right side, it was necessary to connect the right wheel drive and carry out, as they say in relation to trucks, a “power take-off” to drive the rear axle.
Working principle of the coupling
General view of a multi-plate friction clutch
The main task of a multi-disc clutch is to smoothly connect and disconnect the input (drive) and output (driven) shafts at the right moment using the friction force between the discs. In this case, torque is transmitted from one shaft to another. The discs are compressed due to fluid pressure.
Note that the more the surfaces of the disks are in contact, the greater the magnitude of the transmitted torque. During operation, the clutch may slip, but the driven shaft accelerates smoothly, without jerks or impacts.
The main difference between a multi-disc mechanism and others is that by increasing the number of discs, the number of contacting surfaces increases, as a result of which it becomes possible to transmit more torque.
The basis for the normal operation of a friction clutch is the presence of a regulated gap between the discs. This interval must be equal to the value set by the manufacturer. If the gap between the clutch discs is less than specified, the clutches will be constantly in a “prestressed” state and, accordingly, will wear out faster. If the distance is greater, then slipping of the clutch will be observed during operation. In this case, too, rapid wear cannot be avoided. Precise adjustment of the gaps between the clutches when repairing the clutch is the key to its proper operation.
Materials used
Friction clutches are subject to repeated use every day and therefore must have extremely high wear resistance. Today, the most acceptable materials for such units are the following:
- Retinax is a wear- and heat-resistant material, which is made from asbestos and barite based on phenol-formaldehyde resin, reinforced with brass shavings. Works well in units at temperatures up to +700°C.
- The press composition is a wear-resistant material based on phenol-formaldehyde resin, consisting of hexamethelenetetramine reinforced with various fibrous fillers. Operating temperature is up to +190 °C.
- Tribonite is a wear-resistant composite material that can be used in aggressive environments (water, steam, oil products). Operating temperature range from -62 to + 300 °C.
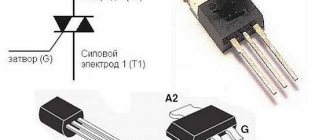
Technical features of the coupling:
- The clutch transmits torque in both forward and reverse gear, because The grooves that wedge the balls are made symmetrical.
- For the clutch to operate, there needs to be at least a slight “lag” between the rear wheels and the front wheels.
- The electromagnet is controlled by applying voltage pulses; the force is adjusted using width modulation of these pulses.
- When incomplete power is supplied to the electromagnet, the clutch provides incomplete closure and is capable of turning.
- When voltage is fully applied, even a fully closed clutch can transmit a torque limited by the friction forces in the clutch.
- There are no temperature sensors in the clutch, and it turns off “due to overheating” when the control unit “sees” for quite a long time through the ABS sensors that, with full power to the clutch, the rear wheels still do not rotate, but the front wheels rotate at a significant speed.
Protective elements, electromagnetic friction multi-plate clutches
A similar electric coupling is very often installed on machines with a numerical control unit. The advantages include the following:
- Compactness. Thanks to this, it is possible to install an electromagnetic coupling in modern devices. From year to year, the dimensions of the device become significantly smaller, which makes the area of use wider.
- Reliability. This parameter is the most important when selecting virtually any coupling. The use of special materials and quality control at all production stages makes it possible to achieve the highest level of reliability.
- Compactness. This parameter determines ease of transportation and other positive parameters.
This embodiment is distinguished by rather large performance characteristics, thanks to which it has become widespread. The significant parts of the structure can be called:
- Frame. In many cases, it is made using steel, which is very resistant to environmental influences. The purpose of the housing is to protect the internal components.
- Coil. Such an element is intended to directly create an electromagnetic field, due to which the displacement of important elements occurs. A coil that is designed to handle a specific electrical current will have an adverse effect if the voltage is too high.
- Friction type disc group. During the manufacture of the friction disc package, a specialized alloy is used, which has some magnetic properties.
- Leash and pressure plate.
- The body has a mounted ring made of insulation material.
- The current is supplied using a contact brush. In many cases, it fails during the operation of the mechanism.
You can eliminate the possibility of a short circuit by using cut holes in the disks. At the moment the electric current is applied, an electromagnetic field is created, which is closed using a friction disk. Actually, thanks to this, an attractive force is created, behind which a displacement of the weighty part occurs.
There are a couple of options for similar designs. An example is a device with a remote and magnetically conductive disk.
DVRs 2018-2019 rating of the best according to customer reviews
Features of operating a Renault/Nissan all-wheel drive vehicle
- In 2WD mode, no voltage is supplied to the clutch under any driving conditions.
- It is not permissible to install wheels with a smaller outer diameter at the rear. Otherwise, the rear axle will not connect until the front wheels slip significantly.
- Regardless of the enabled transmission control mode, all shafts, all gearboxes, all pairs of gears in the transmission part from the gearbox to the rear wheels of the car always rotate. So you shouldn't expect significant fuel savings in 2WD mode on good roads. And, nevertheless, the most correct mode on the highway in summer is 2WD.
- Operating a vehicle with a locked clutch on asphalt will cause it to heat up and wear out, as well as excessive fuel consumption, tire and transmission wear. According to the instructions, Duster blocks the clutch up to 80 km/h. Nissan X-Trail - up to 40 km/h. Once the threshold is exceeded, the system switches to AUTO mode.
- When towing a trailer, you should increase the pressure in the rear wheels to get at least a little torque on them in AUTO mode.
conclusions
All-wheel drive was something exotic in the early and mid-2000s. Crossovers now make up a significant part of the vehicle fleet. All-wheel drive cars from the Renault-Nissan concern have a not very complex and fairly reliable all-wheel drive. A large number of used spare parts on the market makes repairs easier. Nevertheless, remember that this drive is not used for daily “jeeping”. Its purpose is to sometimes drive where a single-wheel drive car cannot get through. Take care and use your crossover correctly, and it will serve you faithfully for many years.