Types of relays
A priority relay, which divides networks into priority and less important ones, allows you to prevent the occurrence of malfunctions during network overloads in an individual home or small enterprise.
The use of an on-load tap-changer allows you to turn off less important devices when there is an overload in the network
Several types of on-load tap-changers are produced:
- 1- and 3-phase;
- single and multi-channel.
Three-phase devices are also capable of performing the function of phase priority, transferring the load through single-phase channels, preventing asymmetry leading to a complete shutdown of the entire facility.
Multi-channel on-load tap-changers can be used together with different lines.
According to their functional design, devices are divided into relays:
- lower threshold;
- upper threshold.
The high threshold relay is activated when the current increases and is connected in a series connection. A device that operates at a minimum voltage threshold, on the contrary, is connected to the network in a parallel circuit.
Relays are also available that are designed for different switching levels, which can be adjusted for different loads if necessary. In networks with heavy loads, the on-load tap-changer should be combined with a current transformer.
Purpose and operation of the load priority relay
This type of relay is designed for cases where there is not enough power input or the cross-section of the electrical wiring does not allow connecting several powerful household appliances at the same time.
Load priority relay
The load priority relay is used in small enterprises with low power input, and in apartments and houses with old electrical wiring. This device controls the connected power and prevents you from connecting several powerful household appliances at once.
In other words (using the example of the ABB load priority relay), the device has two non-priority load groups and two priority load groups. Priority loads are permanently connected and do not turn off, and non-priority loads, one or two, can be turned off when a specified maximum power is reached.
Typically, any one group should not exceed a load current of 16A. If more power is needed, then the load priority relay group and the electromagnetic starter coil are connected through the contacts of the load priority relay group. If the maximum load current exceeds the maximum value, the first non-priority group is turned off, and if this is not enough, the second non-priority group is turned off.
Single-phase priority relay connection diagram
Only non-switchable load groups remain operational. Every 5 minutes, the connection of the non-priority group is checked, and if the maximum current is within the normal range, the second non-priority group is connected and checked for the maximum current. The time for checking the connection of a non-priority group is selected independently.
Disabled groups are signalized by red LEDs. The device consists of a current transformer, a comparator and executive relays. The current transformer measures the current of the loads, which is compared with the specified power by a comparator.
Connection diagram of a single-phase priority relay with loads through automatic machines
When the maximum current is exceeded, the comparator issues a control signal to the relay, the relay contacts open and the load is de-energized. These load priority relays are panel-mounted and DIN-rail mounted. The power control device is installed after the introductory machine.
For each group, the load is connected through a circuit breaker. There are load priority relays as three-phase or designed for a single-phase network, single-channel and multi-channel. The multi-channel device option has several non-priority groups.
The disadvantage of such power limiting relays is the need to modernize the electrical wiring in order to connect separate lines to each group of load control relays. You can also create multiple levels of power control by cascading these relays.
Connection diagram of a single-phase priority relay with a large load through a starter
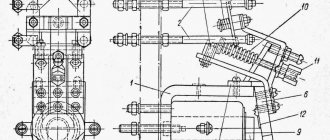
Design
Thanks to the current meter and actuator in the relay, when the current reaches the set value, the contacts are switched. The meter detects current strength in the configured range, and also, depending on the characteristics of consumers, can be configured for switching.
For standard contacts, the maximum switched current is 16A. At enterprises, there is a need to switch larger currents, therefore there is a need to use special contactors.
If magnetic contactors are used, the on-load tap-changer is a separate design and transmits a control signal to the conductor, that is, it does not have the ability to independently switch contacts.
Device
The on-load tap-changer has a built-in current meter and an actuator that switches contacts when a threshold current value is reached and with a specified time delay. The built-in measuring element can monitor the current within a certain range, depending on the specific type of device.
As for the maximum current switched by the built-in contacts, it usually has a standard value of 16 A. If it is necessary to switch high currents, contactors (magnetic starters) are used - in this case, the priority relay will only supply a control pulse to the contactor.
For the need to control large currents, there are certain types of devices that allow you to connect external current transformers. On-load tap changers can be either single-phase or three-phase, and depending on the number of loads controlled, they are divided into single-channel and multi-channel.
Three-phase devices can operate as phase priority relays, switching single-phase loads between phases to prevent large phase imbalances or to prevent line de-energization when one of the phases in the electrical network is broken.
Scope of application
The on-load tap-changer is necessary for the comfortable operation of all electrical consumers connected to one input of the power supply network with a limited power limit. This applies to apartment buildings, old mansions and housing. This problem is especially relevant for village electrical networks remote from centralized sources of electricity.
Often regional networks have limited capabilities. With high power consumption, the voltage drops catastrophically and the probability of the input circuit breaker triggering increases. In those days, when the device had not yet been invented, residents had to decide for themselves what should be manually turned off for the functioning of the necessary electrical appliances. The RPN solved this problem. Installing such a relay is advisable when the input circuit breaker is frequently turned off. An unexpected power outage can create unpleasant and sometimes even dangerous situations.
The priority relay is indispensable in those enterprises whose managers strive for maximum energy savings while maintaining the existing network power. So, for example, if a strict power limit is introduced for a certain group of consumers, then the device will turn off this particular group in critical situations.
Using a load priority relay: we analyze the principle of operation and design of the device
There is a special device that turns on and off the loads in the electrical network in accordance with their value. This device is called a load priority relay.
It can be used both in everyday life and in industry. We invite you to familiarize yourself with what this mechanism is, how it functions and what its application is.
This device works where many electricity users cannot be connected to the network because it has a power limit.
The relay is connected in this case in order to be able to manage groups of network users so that it does not overload and shut down.
Another case when this relay is used is when it is necessary to narrow the use of energy in a certain section of the network. For example, if another consumer is added, and the load on the network is weak.
In both cases, the meaning of the operation of the load relay is the same. It does not allow the machine to turn off the voltage due to network congestion, and leaves the first most important user operational.
Let's consider what a load priority device is.
The load priority relay is a mechanism that consists of a measuring device and an actuator.
The load measuring element monitors the current indicator in a certain amount, which depends on the type of device.
At the same time, the executive part of the device switches the contacts when the maximum current is reached and after a certain time range has passed, which was set in advance.
Typically, the maximum current at which the described device operates is 16 A.
If you need to switch current with a value of more than 16 A, then contactors are used. In this case, the relay will send a control signal specifically to the contactor.
When monitoring high voltages, special types of devices are usually used to which additional transformers can be connected.
Load priority relays are multi-phase and single-phase, and they can also be multi-channel or single-channel.
Multiphase load priority relays can also be used as phase priority relays. In this case, it switches the voltage between phases when there is a risk of tripping the line due to phase failure or phase mismatch.
So, at the beginning of the network, a machine with a voltage of 25A is installed at the input, while the actual voltage of the electrical network is much higher than this figure.
Next, a device is installed that has two channels, which prevents the network from being overloaded by turning on or off two levels of load.
In our scheme, the first group has priority in work, and it is always energized.
The remaining two groups are immediately switched off at the slightest increase in the set voltage, in our example this value is 25 A.
Of these two groups, the third one, with the lowest priority, will be turned off first. If the reduction in current is not enough for the operation of two groups, then after the third the second one will turn off, creating all the operating conditions for the first, highest priority group.
After stabilizing the current strength in the network using the load priority relay, the second, and then the third group of network users will return to work.
As for the practical application of the device described above, the most common example of its use in everyday life is our ordinary home.
So, if there is a limit on current consumption in an apartment or house, this will not allow you to turn on all the household electrical appliances you need at the same time.
Then the load priority relay comes into operation. It gives you the opportunity to use household appliances in a way that is convenient for you, without any problems.
If this regulator is not connected, then there is a possibility that the wiring of your home will completely stop functioning when the voltage in the network increases, which is regulated by a machine or device that limits the current.
Or, as an option, you will need to alternately turn on and off electrical mechanisms yourself according to the priority of their work, which is very inconvenient in today’s world of high technology.
After several cases of sudden network shutdown due to high load, you will fully experience the usefulness of such a load distribution priority device as the relay we are describing.
After all, an unscheduled shutdown of machines can damage electrical appliances. It is also inconvenient that you can often turn on the circuit breaker only after it has completely cooled down after overheating.
The same scheme of operation of priority relays is also used in industry. With its help, large enterprises can use many devices with limited current in the network, which saves them from the need to increase it.
It also helps support the energy-saving operating concept of industrial plants.
So, for example, if a certain maximum rate of electricity consumption is set, then the priority relay at the right time will automatically turn off devices that are not involved in operation in the set time range, but consume electricity.
In this way, the maximum possible savings in electrical energy consumption at the enterprise will be achieved.
The operating principle of this priority device can be seen in more detail in the video below:
This concludes our story about load priority relays.
We hope that we have clearly and thoroughly described the operation of this mechanism and that this acquired knowledge will help you in the future!
Application area
Considered the most essential power line, it must be connected at all times. Non-priority lines are those whose disconnection from the network in case of overload will not lead to any consequences.
In case of overloads, lighting important for the safety of the enterprise will not be switched off, but only consumers on the line with low priority will be switched off. When normal network operation is restored, all non-priority consumers will automatically connect.
If an overload occurs due to the switching on of several devices, it is possible to turn off only one of them. At the same time, power supply to high-priority consumers will be restored.
Current monitoring devices
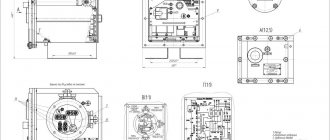
RMT – 101 – AC relay is used to measure and control the effective value of single-phase load current in the range from 0 to 100A.
The device is widely used as:
- Digital ammeter;
- Current limit relay;
- Priority load relay.
The LED display shows the measured load current value. Indicators on the front panel display the load status (on/off), as well as an overcurrent alarm of the three-phase current relay setting - the on/off parameter is displayed, as well as an indicator that the maximum current value has been exceeded.
In addition to setting the maximum value of the load current, the device allows you to set the shutdown time delay when an accident occurs, as well as the time delay to turn on the load after the current value is restored.
RMT – 104 – the device is designed to monitor the effective values of single-phase load current in the range from 1 to 400A. If the parameters specified by the user are exceeded, the load is disconnected. The device is equipped with an independent time delay function and further automatic reclosure (AR) or blocking. The user can set the parameters for restarting independently using the potentiometers on the front panel of the device.
Types of on-load tap changers and design features
A current meter is built into the on-load tap-changer design. Thanks to it and the actuator, contacts are switched at moments when the current value reaches a threshold level. The measuring element determines the current strength in a certain range, and it can also be configured to switch based on specific network consumers and their technical characteristics.
The maximum value of the switched current for standard contacts is 16 A. In production, there is a need to switch high currents, for this purpose special contactors are used.
When using magnetic starters, the priority relay is separated into a separate structure and does not switch contacts independently, but only transmits a control signal to the contactor.
Devices for monitoring high voltage currents are classified as a separate group and differ in design from conventional on-load tap-changers and allow the use of external current transformers.
Based on the number of controlled loads, the on-load tap-changers are:
- single-phase;
- three-phase - allow the device to act as a phase priority relay; they switch the load through single-phase channels, preventing asymmetry leading to de-energization of the entire facility.
Depending on the number of loads, the on-load tap-changer can be:
- multichannel;
- single-channel.
Model overview
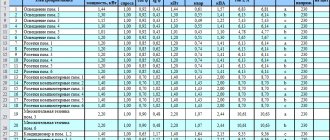
The table shows the most popular relay brands among domestic buyers, indicating the main characteristics and estimated cost.
The choice of one model or another is determined not so much by the price as by the operating conditions of the relay and its connection diagram.
| Brand | Main characteristics | Approximate cost, rub. |
| ABB LSS1/2 | Voltage - 230 V ∼ ± 20% Highest priority load current 90 A Current range, A 5…90 Settable current ranges, A 5…30, 10…60, 15…90 | 2000 |
| Legrand 0 038 11 | Currents of low-priority loads - up to 15A Shutdown threshold, 15 - 20 - 25 - 30 - 40 - 50 - 60A The total current of connected consumers is 90A Number of modules - 5 | 1800 |
| CDS Schneider Electric | Current range: configurable priority channel from 5 to 90 A, low priority channels - 15 A. Voltage range: 240 VA +5%, -10% Frequency: 50/60 Hz. | 2200 |
| F&F PR-612 | Maximum priority load current - 16 A Maximum non-priority load current 15 A Low-priority circuit shutdown current adjustment interval 2 - 15 A | 1900 |
| Z–LAR/8 | Rated voltage 250 V Switching current >3 A Tripping current < 1.8 A Switching frequency - up to 3600/h | 1750 |
Disadvantages of using on-load tap changers and its analogues
Despite the large number of advantages associated with connecting and using load priority relays, using the device also has some disadvantages:
- To install a device into an existing network, it is necessary to perform a large amount of work related to upgrading the wiring and panel. To do this, it is necessary to invite a qualified specialist who will make an accurate calculation of the circuit in accordance with the load from all existing consumers.
- To lay separate cable lines from the switchboard to sockets with various consumers, it is necessary to wall groove and repair the premises.
- On-load tap changers are not installed on regular wiring, the design of which does not provide for the presence of separate lines to sockets.
Dividing lines into priority ones in everyday life has become easier thanks to the introduction of a new device - a network load optimizer, which also turns off non-priority electrical appliances.
The operating principle of the optimizer is to redistribute the power of consumers in accordance with their degree of importance. While the priority electrical appliance is turned on, the optimizer turns off the lower priority device, which turns on again during a pause in the operation of the higher priority one.
Disadvantages of using a load priority relay
Disadvantages of using this device:
- Installing a relay is a very labor-intensive process. A simple consumer will not be able to produce such a volume of work. In this case, it is necessary to reconstruct the wiring and distribution panel. For this purpose, you should use the services of a specialist who will make the correct calculation of the wiring in relation to the consumed load of the connected electrical appliances.
- The installation process involves chipping the walls and, as a result, restoring them. The process of installing a voltage relay is expensive, as it requires some financial investments.
- At the same time, to install the mechanism, you need to purchase specialized cables and conduct separate wiring to the sockets. Regular wire will not work for this purpose.
Load priority relay device
Disadvantages of using on-load tap changers
Despite the rather extensive list of advantageous features, the on-load tap-changer also has disadvantages:
- It is not possible to install a priority relay on ordinary wiring, the circuit of which is not equipped with separate lines to sockets.
- To install a device into an existing network, it is necessary to perform a lot of work that involves upgrading the wiring.
To install separate wiring lines from the distribution panel, you will need to trench the walls, so repairs throughout the entire room cannot be avoided. This approach requires considerable financial costs, time and effort.
Typical mistakes when connecting an on-load tap-changer
- A common mistake is the incorrect grouping of loads from consumers according to their degree of importance. It is not uncommon for the owner of an apartment, house or director of an enterprise to not clearly understand the priority of a particular household electrical appliance, machine, or piece of equipment. To avoid such a burden, it is recommended to invite a professional for consultation.
- Another mistake leading to serious consequences is connecting loads directly to the on-load tap-changer (with a maximum device load of up to 16A), and not through contactors. The reason for this may be either simple inattention, or an insufficient level of knowledge in electrical engineering and neglect of the recommendations of the relay manufacturer.
- Often, inexperienced electricians make a mistake related to the supply of phase to the on-load tap-changer contacts intended for connecting indicator lamps.
Types
The most common types of phase control relays, which are mainly used in production and in domestic conditions, are EL11, EL12, EL13 and EL11MT, EL-12MT.
To protect power supplies, automatic transfer switches, generators and power converters, EL11 and EL11MT are used.
To ensure the safety of crane electric motors with a power of up to 100 kW, EL-12 and EL12MT are used.
EL13 is mainly used when connecting reversible electric motors up to 75 kW.
These relays can be mounted using either a DIN rail or mounting screws.
Why do you need a load priority relay?
- Load priority relay (LPR) is a device designed to turn off and turn on loads in the electrical network depending on their importance. This device is often used both in domestic conditions and in enterprises. Let us briefly consider what this device is, its operating principle and purpose.
The priority relay is used to control groups of consumers in electrical networks in which the maximum power consumption is limited and does not allow all necessary consumers of electrical energy to be connected to the network at the same time.
This device can also act as a power limiting relay in cases where it is necessary to limit the current flowing through a particular section of the circuit, for example, when adding new electrical consumers to a network that has insufficient load capacity.
In both cases, the use of a load priority relay allows you to avoid tripping the circuit breaker due to overload, leaving the most important consumers in operation.